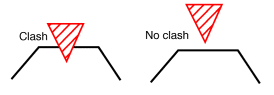
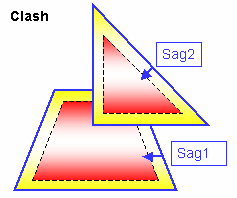
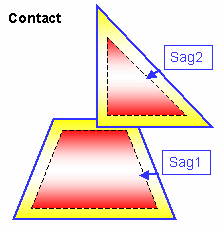
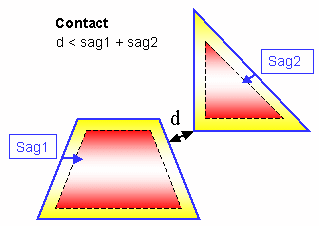
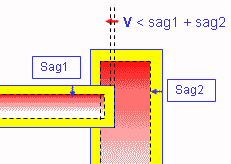
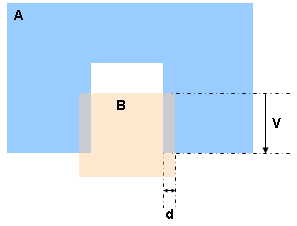
You can check your document for clash, contact and clearance conflicts to determine whether document components interfere with each other.
Depending on your needs, you can choose between different levels of analysis, ranging from a simple detection of interferences between parts (Analyze > Part to Part Clash) to a detailed clash, contact and clearance analysis of products and/or elements (Clash command). Note that only visible parts and products are taken into account; interference checking is not done on parts and products in the No Show space. Results differ depending on the interference type selected for the analysis.
You can analyze Clash command
results using a variety of tools and visually browse interferences in a
preview window or separate viewer. You can
also export and publish results in text, XML
and HTML formats.
As part of a standalone clash process, you can export both clash results and geometry to a dedicated file-based database. Results and geometry are managed in XML files. You can then import these results back into your session.
The following section deals with:
Creating Groups of
Products
In DMU-P2, prior to running your interference analysis, you
can create groups containing the product(s) you want to analyze using the
Group
![]() icon in the DMU Space Analysis toolbar or Insert -> Group... in
the menu bar.
icon in the DMU Space Analysis toolbar or Insert -> Group... in
the menu bar.
Groups created are identified in the specification tree and can be selected from there for the analysis. Only one group per selection can be defined.
ENOVIA
Integration
When working with ENOVIA LCA, the user can send the clash
object directly from the ENOVIA query panel to CATIA. The clash result is
re-created in the CATIA session. To import the products involved and
visualize the clash, simply click the appropriate interference line in the
Check Clash dialog box.
You can also
compare
clash results with those stored in ENOVIA VPM or ENOVIA LCA.