![]()
A behavior is a set of tasks performed on a technological object. It can be a V5 command, a CAA command, an external application, a VBA Command, or a behavior defined in BKT. It enables expert users to capture sequences of tasks that are manually performed in V5, and enables end-users to use the knowledge contained in the behaviors to perform tasks and procedures related to the technological object.
A behavior is made up of the following components:
|
Name displayed in the end-user workbench. The comment associated with this name can help the end-user understand the behavior function. | |
|
Inputs: Data entered by the user Outputs: Result produced by the behavior Internals: Defined for internal use as storage of intermediate results |
|
|
Icons ... |
To define a new behavior, the expert user:
|
|
Structure Behaviors (Logical and Sequential
Combinations)
|
Enable you to define two different
combinations of behaviors:
|
|||||
|
Infrastructure Behaviors
|
Implementation Behaviors: Enable
you to reuse existing code samples. Bind Behaviors: Enable you to access resources not yet available at the definition stage. |
|||||
| Event-based Behaviors | Enable you to define what element reacts and how it reacts when something happens. | |||||
| Design Behaviors | Enable you to reuse CATIA V5
functions.
Insert Components: Enables you to create a component, or to insert an existing one taking the multioccurrence into account. |
|||||
| Knowledge Relations | Enable you to define rules, checks and formulas that need to be validated during the process or add logical control to the model. |
| Note that it is now possible for the user to add attributes of List type to behaviors. For more information, see About the Add Attribute dialog box... |
The Behaviors interface is made up of 2 or 3 tabs depending on the behaviors:
|
|
|
The Definition tab contains the information that needs to be specified for the behavior to execute correctly. For more information about this tab (specific to every behavior), see the documentation related to the various behaviors.
The Properties tab
This tab contains the information required for the behavior execution.
|
Behavior States
Activate: If not checked, the behavior will not be part of the execution process. AutoDelete: If checked, the expert user does not want to keep track of the behavior execution and the behavior is removed after it is executed. Focus: If checked, no other behavior asking for the focus will be started till the current behavior is executed. Update |
|||
|
Icon Definition This field enables the expert user to modify the icon identifying the Behavior in the behaviors tree and in the user workbench. A set of icons is available from Icons.... If you click this button, the Icon Browser opens showing all icons loaded in your CATIA session. To associate an icon with a technological object, define a name: I_nametype. For example for the technological object Interior, the icon name is: I_Interior. To save the created icons in the appropriate directory, see Setting up the working Environment. |
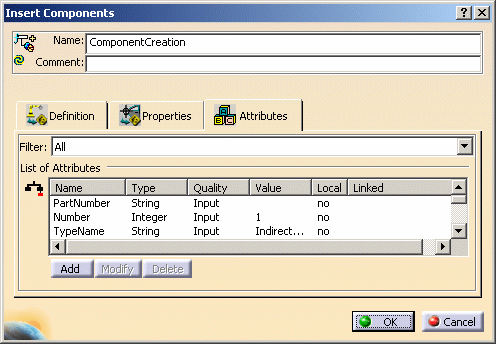
The Attributes tab
|
Filter Local attributes are those defined by the expert user. The other attributes are defined by default.
List of Attributes The parameters displayed in this field are the ones displayed in the behaviors tree. The BState parameter, when available, indicates the status of the behavior's child.
For a logical or a sequential combination, the name of the behavior that was last run is displayed in this field. |
|||||||||
Note that:
The behavior is also provided with a property defining if it
can execute or not. If the inputs are not valuated, this behavior cannot
operate (![]() ).
).
Behaviors attributes can be accessed by clicking the Attributes tab in the behaviors interfaces or below the behaviors in the Behaviors tree.
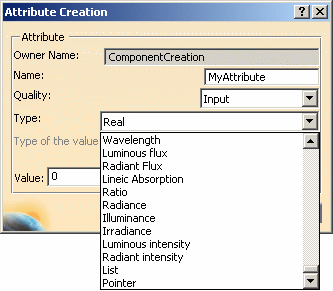 |
Pointers, and Lists can be typed to specialize the
pointed items. If the value stored in the Pointer and the List does not
match the selected type, an error message is displayed when operating or
editing the behavior. Note that Pointer, and List attributes can be
typed: Those created by the user as well as those belonging to the
behaviors.
To type a Pointer, or a List attribute:
For more information about the packages and types of this browser, see the Reference section of the Knowledge Expert User's Guide. |
Creating Behaviors
Linking Behaviors
Combining Behaviors
Working with Behaviors Patterns
Reference Information