A sensor is a physical output of a computation, optionally
limited to a local area, on which you can apply a post-treatment.
You can get a synthesis of analysis results by
creating sensors.
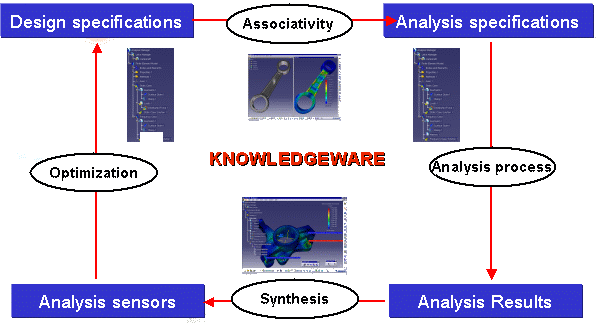
A sensor can produce two kinds of results, depending on the sensor definition and on the analysis case:
- knowledge parameters (single value or list of values): the sensor set provides parameters that can be re-used in Knowledgeware in order to set rules, checks, formulas and Product Engineering Optimizer workbench.
- 2D Display (only in multi-occurrence case): allows you to display the
variation of an output for different occurrences.
- Create Global Sensors
- Create sensors on entire model.
- Create Local Sensors
- Create sensors on local area.
Resultant Sensors
- Create Reaction Sensors
- Create a reaction sensor.
- Create Applied Load Sensors
- Create applied load sensors.

- Create Multi Load Sensors
- Create multi load sensors.

- Create Internal Load Sensors
- Create internal load sensors.

- Create Inertia Sensors
- Create inertia sensors.

Update Sensors- Update all the sensors belonging to a sensor set or update a particular sensor.
- Display Values of Sensors
- Display values of sensors in the specification tree under a sensor set.
- Integration with Product Engineering Optimizer
- Give information about the analysis data authorized in the Product Engineering Optimizer (PEO) product.