![]()
|
|
This section explains how to use the search language to search for objects. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The
search language offers almost all of the search functions available with
Edit > Search described in Selecting
Using the Search... Command. Searching using this command generates a
search query (expressed in the search language) displayed in the
Generated query box of the Search dialog box. The search language can be used both in the power input box and in the Advanced tab of the Search dialog box but also in macros. The search query both searches for the elements and automatically selects them. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Any generated query
can be run via the power input box or in macros, whether transformat
or not. However, the transformat query is the only usable query whatever the session language, therefore any query you expect to run in different session languages must be written in this format. If you are not familiar with this format, you can display its content and identify the syntax to be used prior to writing your transformat query using a hidden column (you need to drag the column separator next to the Query column to display it) in the Favorites tab of the Search dialog box: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For instance,
CATDrwSearch.DrwText.Name=test,in means that you will search for
objects named "test" in the Drafting workbench using the "In <UI-Active
object>" scope. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This scenario deals with the following sections:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To run a search via the power input box, proceed as follows: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Search Language: Syntax |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for
objects using the same criteria as with Edit > Search. The
message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls sets up the power input search syntax,
and search language shortcuts. The localized version of this message
catalog determines the exact syntax and shortcuts for each language. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using Operating Signs |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The search
language uses the following separators (whose role you will discover in the
examples below):
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Name |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for an object name.
This is particularly useful if you renamed objects using Edit >
Properties, or the Properties contextual command. The name
can also contain special characters. To search for an object by its name, enter the following command:
or a command using an abbreviation referred to as a "shortcut" as follows:
where "object_name" is the name of the object. You can also use the "*" character as a wildcard to replace any number of characters. For example, the command:
searches for all objects starting with the string "wheel". The message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls sets up unambiguous default
shortcuts. For example, there is no ambiguity between the shortcut If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following command:
searches for all objects starting with the string "Wheel". Note: the keyword used for queries that are not case sensitive is
always in lowercase whereas for case sensitive queries, the keyword is in
uppercase. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Name in Graph |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for
an object name. This search is different from searching by name since it
deals with the name as it is displayed in the specification tree. To search for an object by its name as displayed in the specification tree, enter the following command:
If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following command:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
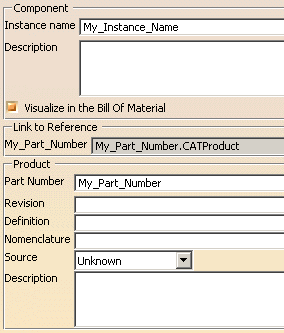
| This name may be customized and thus, may differ from the name you entered in the Properties dialog box. For instance, suppose a part with named "My_Part_Number"... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| whose name is displayed as follows in the specification tree: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
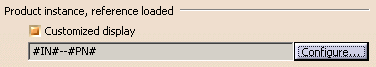
| Let's suppose you customize the display in Tools > Options > Infrastructure > Product Structure > Nodes Customization tab by entering the following data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The name displayed in the specification tree now looks like this: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entering:
gives no result since the search is based on the name displayed in the Instance Name box. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| But entering:
finds the part. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note that the tree item size defined in the Tree Appearance tab is not taken into account. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Type |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use the Type
box in the Search dialog box to display a list of types (the
types are translated in each language). To search for an object by its type, enter the following command:
or:
You can also search for types using the "." (period) as follows: For example, entering the command:
searches for all objects of type Pad created using the Part Design workbench. The following syntax is also allowed:
For example, entering:
searches for all objects of type Pad created using the Part Design workbench, and of the color Sea Green. You can omit the workbench name if the type exists only for this workbench:
and:
are equivalent. Similarly:
and:
are also equivalent. Here are some more examples using other operators described in Using Operators:
and: workbench.type.color='sea
green'
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Color |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You assign colors to objects using
the Color list in the Graphic tab, when using
Edit > Properties or the Properties contextual command.
For a reminder about how to use this list, refer to
Displaying and Editing Graphic Properties. To search for an object of a specific color, enter the following command:
or:
where "color_name" is the color of the object. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| If the
name of the color contains a blank (which is the case with most of the
colors available), you can type the full name as follows:
You can also surround the blank or the color name with a single quote (by default) like this:
or like this:
You can also search for colors using their RGB values. For example:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In addition to
this, each color displayed in the Color list or in the color
palette is identified by an index in the color table. Therefore, when
searching for the "Salmon" color for instance, you can enter either:
or:
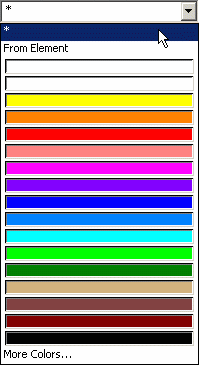
since "Salmon" is the 17th color in the color palette. The 16 colors available in the Color list are: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
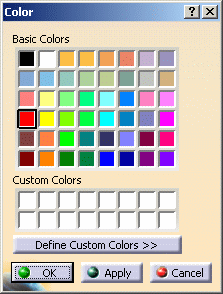
| In the color
palette, 48 colors are provided, among which 16 colors are the same as
those displayed in the Color list. The remaining are extra
colors. These colors are numbered as follows, from top to bottom: on the first row are colors #1 to #8, on the second row are colors #9 to #16 and so on til color #48 in the lower right corner: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To see the table listing the 48 colors along with their name, index and RGB code, refer to Color Palette. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Product Properties |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
You assign properties to products (and parts in products) by right-clicking
an element in the specification tree and selecting
Properties,
clicking the Product tab in the Properties dialog
box, and setting the properties in the Product frame. The properties you can search for (the same as those you assigned to the element) are:
For example, the search queries:
search for all elements whose Product Description is the text "completed". The property name is case sensitive. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching for Objects Belonging to a Layer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To search for an
object belonging to a specific layer (as seen in the Graphic
Properties toolbar), enter the following command:
or
where "layer_number" is the number of the layer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching for Objects Belonging to a Selection Set |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To search for an
object belonging to a selection set, enter the following command:
or
where "selection_set_name" is the name of the selection set. If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following command:
The strings "name", "type", "color" and "set" are appropriate for the
English language only. The message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls determines
the exact syntax for your language. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching for Visible or Hidden Elements |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for
visible, invisible, shown elements, or elements hidden in the No Show space
using the following syntax:
and:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching for Line Thickness or Linetype |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can also
search for objects with a specific line thickness or linetype (as seen in
the Graphic Properties toolbar) like this:
or:
When searching for lines with a specific weight, you can specify the weight index like this:
to search for all lines which are 2.0000 mm thick. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching by Symbol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To search for a
point symbol, enter the following command:
or
searches for the following point symbol:
Capital letters are meaningless for the symbol name and you can also type:
The point symbols you can search for are: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching Using Favorites |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for
objects using your favorite queries defined via the
Favorites tab in the Search dialog
box. To do so:
but you can also enter:
where "favorite_query_name" is the name of the favorite query. Note that the language used in favorite queries is case sensitive. When you press Enter, the search results are selected in the specification tree. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
You can use any of
the special characters such as !. For example, let's
use the query defined in Searching Using the
Favorites Mode. This query searches for any element named "My Sketch".
Now, suppose you want your search to select all elements whose names are
other than "My Sketch", you just have to type:
or
In that case, the search scope is not modified. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To modify the
search scope, indicate the new scope after the favorite query name in the
power input box:
searches for any element named "My Sketch" From Search to bottom and not Everywhere as originally defined in Query_1. The new scope supersedes the previous one. You can also combine favorite queries with predefined favorite queries. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Searching Using Predefined Favorites |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Before you start,
note that these predefined favorite queries (which deal with V5 objects
only) can be neither modified, nor deleted contrary to standard favorite
queries you define in the Favorites tab of the Search
dialog box. The shortcuts used to run these predefined queries have been defined to search "Everywhere". However, if the scr as Visible on screen option is selected in the Default Search Scope for Power Input list and if the Replaces scope defined in favorite queries option is selected, the queries will search for visible elements only. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Search with no selection required |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can search for objects using predefined favorite queries. These predefined queries are run by entering the following shortcuts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For instance, to
search for all sketches everywhere, enter the appropriate shortcut after
the prefix used to run favorite queries:
but you can also enter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
If the option f:
as favorite: is selected in the
Default Prefix for Power Input list, you do not need to type the prefix
before the shortcut. You simply enter:
to search for all sketches everywhere. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Search with selection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predefined shortcuts are provided to search for elements having a characteristic in common with the element you select: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| To run a
predefined favorite query involving a selection, you need to select the
object before or after entering the appropriate shortcut. For instance, to search for all objects with the same color as the selected object ("blue" in our example), select a "blue" object then enter:
or enter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Select the object then click Close to close the acquisition agent. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Search with arguments |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| You can run predefined favorite queries with arguments. These predefined queries are run using the following shortcuts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For instance, to
search for all lines of type "Dotted" everywhere, enter the appropriate
shortcut after the prefix used to run favorite queries:
but you can also enter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
If the option f:
as favorite: is selected in the
Default Prefix for Power Input list, you do not need to type the prefix
before the shortcut. You simply enter:
to search for all lines of type "Dotted" everywhere. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using Special Characters |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Characters
& + - ( ) play a
special role in the search syntax:To be interpreted literally in names, those characters or text strings containing those characters must be surrounded by the character '(apostrophe by default).For example:
The following line in the KeyboardInput.CATNls resource file :
specifies the default character for surrounding strings. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The
character * is always interpreted as a wild card except if surrounded by
two characters '. For example:
n:*')' |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The
character ' must be doubled twice to be interpreted literally. For example:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using Operators |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The supported
operators are: &, +, and - (for AND,
OR and EXCEPT respectively) and ( ).
Blanks are not considered as separators. They
may be surrounded by |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining standard queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The following
examples:
all search for parts whose names end with "wheel&door". The command:
searches for objects named "wheel1" and objects named "wheel2". |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining predefined favorite queries, favorite queries and standard queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Before you start,
note the following information:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
You can try by yourself the sample combinations provided below using the Search1.CATProduct document. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining predefined favorite queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Let's suppose you
want to search for all lines or all points. You enter:
but you can also use any other favorite prefix ( This query searches for all lines and points everywhere since no scope has been specified and, as explained above, the scope of the predefined query is used. If you want to use another search scope, you need to specify it after the query. For instance, to search for all lines and points visible on screen, you can either set scr as Visible on screen as the default scope in the Default Search Scope for Power Input list (do not forget to select the Replaces scope defined in favorite queries option as well) or enter:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining predefined favorite queries and favorite queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Let's suppose a
favorite query named "Query_1". This query searches for all elements whose
color is "black". If you want your search to select all lines and whose color is "black", you just have to type:
but you can also use any other favorite prefix ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining predefined favorite queries and standard queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Let's suppose you
want to search for all sketches except those whose name ends with
"1". You enter:
but you can also use any other favorite prefix ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Combining predefined favorite queries, favorite queries and standard queries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Still using a
favorite query named "Query_1" (which searches for all elements whose color
is "black"), let's suppose you want to search for all lines and
whose color is black or whose name ends with "3". You enter:
but you can also use any other favorite prefix ( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Priority |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| There is no priority among
operators, but there is a priority in their order of appearance (from left
to right). For example, the query:
is interpreted as: type:Part* & (name:toto +
(type:Hole & Color:Black) )
and thus searches
for elements of type "Part" among the objects in the document that are
"black holes" or named "toto".
To avoid ambiguity,
use parentheses like this:
type:Part* & (name:toto + (type:Hole & Color:Black) )
to obtain the same result. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using Search Scopes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
You can use the same search scopes
as with Edit > Search (except From search results
which is only available in the Search dialog box) , by using the
context aliases all, in, from,
sel and :
The default is
The separator is the comma (",") for the English, Japanese, Korean and simplified Chinese environments, and the semi-colon (";") for all other supported environments. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using a Default Prefix |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A prefix is
required to run a command or a query via the power input box. One prefix (c:)
is already provided to run commands and several prefixes are dedicated to
search queries.When searching for a name for instance, the value you type must be prefixed by n: or with name:, e.g. n:wheel.
By default, no default prefix is defined. But if you use a default prefix,
this avoids having to type the prefix when entering your query in the power
input box, you just have to enter the search string. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Suppose you select
the prefix n: as name: in the Default Prefix for Power
Input list then in the power input box, you enter only the name you
are searching for such as:
to search for objects named "wheel". |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using a Default Search Scope |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
As explained above
in Using Search Scopes, the default scope
is in when running a query in the power input box. This means
that if no scope alias is entered at the end of the search string, the
search locates the appropriate elements in the active object and in the
workbench you are currently using.Using a default search scope avoids having to type the scope in the power input box. The default search scope is defined in the Search tab which provides a list of predefined search scopes. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For instance, if
the scope all as Everywhere is selected in the Default
Search Scope for Power Input list, you just need to enter:
instead of
to search for objects of type "Hole" in the whole specification tree from top to bottom. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||