This section contains information about diagnosing common problems in a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network environment.
The netstat command is a good tool for determining which area of the network has a problem. Once you have isolated the problem to an area, you can use more sophisticated tools to proceed. For example, you might use the netstat -i and netstat -v to determine if you have a problem with a particular hardware interface, and then run diagnostics to further isolate the problem. Or, if the netstat -s command shows that there are protocol errors, you could then use the trpt or iptrace commands.
The topics discussed in this section are:
If you cannot communicate with a host on your network:
If the name resolves and you are trying to contact a host on another network, you may have a routing problem. See "Routing Problems" for more information.
Resolver routines on hosts running TCP/IP attempt to resolve names, using the following sources in the order listed:
When NIS+ is installed, lookup preferences are set using the irs.conf file. For more information, see AIX 5L Version 5.1 Network Information Services (NIS and NIS+) Guide.
If you cannot get a host name resolved, and you are using flat name resolution (using the /etc/hosts file), verify that the host name and correct Internet Protocol (IP) address information is in the /etc/hosts file.
If you cannot get a host name resolved, and you are using a name server:
If these steps do not identify the problem, check the name server host.
If you cannot get a host name resolved:
lssrc -s named
Add or correct name-to-address resolution information in the named hosts data file for the master name server of the domain. Then issue the following SRC command to reread the data files:
refresh -s named
startsrc -s named -a "-d DebugLevel"
Note: A common error is the incorrect use of the . (period) and the @ (at sign) in the DOMAIN data files.
If external users cannot reach your domains:
If external resolvers query your servers constantly:
If you cannot reach a destination host, consider the following situations:
Note: Make sure the host you want to communicate with has a routing table entry to your machine.
Note: You need to do this only if the routing daemon cannot identify the route to a distant host through queries to other gateways.
startsrc -s routed -a "-d"
If all else fails, you might want to turn on tracing for your routing daemon (either routed or gated). Use the SRC traceson command from the command line, or send a signal to the daemon to specify different levels of tracing. See the gated daemon or the routed daemon for specifics on sending signals to these daemons.
Update the inetd daemon by issuing the refresh -s inetd command or the kill -1 InetdPID command.
0513-00 The System Resource Controller is not active.
The System Resource Controller subsystem has not been activated. Issue the srcmstr & command to start SRC, then reissue the startsrc command.
You might also want to try starting the daemon from the command line without SRC support.
[subsystem name] does not support this option.
The subsystem does not support the SRC option issued. Check the subsystem documentation to verify options the subsystem supports.
SRC was not found, continuing without SRC support.
A daemon was invoked directly from the command line instead of using the startsrc command. This is not a problem. However, SRC commands, such as stopsrc and refresh, will not manipulate a subsystem that is invoked directly.
If the inetd daemon is up and running correctly and the appropriate service seems to be correct but you still cannot connect, try running the inetd daemon processes through a debugger.
stopsrc -s inetd
The stopsrc command stops subsystems like the inetd daemon.
vi /etc/syslog.conf
refresh -s syslogd
kill -1 `ps -e | grep /etc/syslogd | cut -c1-7`
startsrc -s inetd -a "-d"
The -d flag enables debugging.
tn bastet Trying... connected to bastet login:> Connection closed
tail -f /tmp/myfile
The following explanations can be useful in solving problems with the telnet or rlogin command.
If you are having trouble with screen distortion in full-screen applications:
env
echo $TERM
telnet subcommands that
can help in debugging problems include:
| display | Displays set and toggle values. |
| toggle | Toggles the display of all network data in hex. |
| toggle options | Toggles the display of internal telnet process options. |
If the inetd daemon could execute the telnet service but you still cannot connect using the telnet command, there may be something wrong with the telnet interface.
telnet tn>
telnet bastet Trying... Connected to bastet Escape character is '^T'.
Watch the display as the various commands scroll up the screen. For example:
SENT do ECHO SENT do SUPPRESS GO AHEAD SENT will TERMINAL TYPE (reply) SENT do SUPPORT SAK SENT will SUPPORT SAK (reply) RCVD do TERMINAL TYPE (don't reply) RCVD will ECHO (don't reply) RCVD will SUPPRESS GO AHEAD (don't reply) RCVD wont SUPPORT SAK (reply) SENT dont SUPPORT SAK (reply) RCVD do SUPPORT SAK (don't reply) SENT suboption TELOPT_NAWS Width 80, Height 25 RCVD suboption TELOPT_TTYPE SEND RCVD suboption TELOPT_TTYPE aixterm ...
ls -a /usr/lib/terminfo
tic ibm.ti
The tic command is a terminal information compiler.
Problems with function and arrow keys can arise when using the rlogin and telnet commands with programs using extended curses. Function and arrow keys generate escape sequences, which are split if too little time is allotted for the entire key sequence. Curses waits a specific amount of time to decide whether an Esc indicates the escape key only or the start of a multibyte escape sequence generated by other keys, such as cursor keys, the action key, and function keys.
If no data, or data that is not valid, follows the Esc in the allotted amount of time, curses decides that the Esc is the escape key, and the key sequence is split. The delay resulting from the rlogin or telnet command is network dependent. Sometimes arrow and function keys work and sometimes they do not, depending on the speed of the network to which you are connecting. Setting the ESCDELAY environment variable to a large value (1000 to 1500) effectively solves this problem.
Network interfaces are automatically configured during the first system startup after the adapter card is installed. However, you still need to set some initial values for TCP/IP including the host name, the Internet address, and the subnet mask. To do this, you can use the Web-based System Manager, wsm, or you can use the SMIT interface in the following ways:
You may also want to set up any static routes the host needs for sending transmitting information, such as a route to the local gateway. Use the Web-based System Manager, wsm, or the SMIT fast path, smit mkroute, to set these up permanently in the configuration database.
If you are having other problems with your configuration, see the "Configuring a TCP/IP Network Checklist" for more information.
Network interfaces are configured automatically during the first system startup after the adapter card is installed. However, there are certain values that must be set in order for TCP/IP to start. These include the host name and Internet address and can be set using the Web-based System Manager, wsm, or the SMIT fast path, smit mktcpip.
If you choose the SMIT method, use the smit mktcpip fast path to set these values permanently in the configuration database. Use the smit chinet and smit hostname fast paths to change them in a running system. The smit mktcpip fast path minimally configures TCP/IP. To add adapters, use the Further Configuration menu, which can be reached with the smit tcpip fast path.
If you have already checked these to verify accuracy and you are still having trouble sending and receiving information, check the following:
arp -a
The arp command looks for the physical adapter address. This command might show an incomplete address. For example:
? (192.100.61.210) at (incomplete)
This could be due to an unplugged machine, a stray address with no machine at that particular address, or a hardware problem (such as a machine that connects and receives packets but is not able to send packets back).
netstat -v
The netstat -v command shows statistics for the Ethernet, Token Ring, X.25, and 802.3 adapter device drivers. The command also shows network and error logging data for all device drivers active on an interface including: No Mbufs Errors, No Mbuf Extension Errors, and Packets Transmitted and Adapter Errors Detected.
If these steps do not identify the problem, see "Problems with a SLIP Network Interface", "Problems with an Ethernet Network Interface", or "Problems with a Token-Ring Network Interface".
In general, the most effective method for debugging problems with a Serial Line Interface Protocol (SLIP) interface is to retrace your configuration, verifying each step. However, you can also:
Select the SLIP interface. Make sure that the INTERNET ADDRESS and DESTINATION Address fields are correct.
If the modem is not functioning correctly:
If the tty is not functioning correctly, verify that the tty baud rate and modem characteristics are set correctly in the configuration database by entering the smit tty fast path.
If the network interface has been initialized, the addresses correctly specified, and you have verified that the adapter card is good:
If you cannot communicate with some of the machines on your network although the network interface has been initialized, the addresses correctly specified, and you have verified that the adapter card is good:
If you cannot communicate between a token-ring and an Ethernet network, using a bridge, and you have verified that the bridge is functioning correctly, the Ethernet adapter might be dropping packets. A machine drops packets if the incoming packet (including headers) is greater than the network adapter maximum transmission unit (MTU) value. For instance, a 1500-byte packet sent by a token-ring adapter over the bridge collects an 8-byte logical link control (LLC) header, making the total packet size 1508. If the receiving Ethernet adapter MTU is set to 1500, the packet is dropped.
Check the MTU values of both network adapters. To allow for the eight-byte LLL header, the token-ring adapter attaches to outgoing packets, set the MTU value for the token-ring adapter at least eight bytes lower than the MTU value for the Ethernet adapter. For example, set the MTU for a token-ring adapter to 1492 to communicate with an Ethernet adapter with an MTU of 1500.
When operating through a bridge, change the default value of 1500 for the maximum transmission unit (MTU) to a value that is eight less than the maximum information field (maximum I-frame) advertised by the bridge in the routing control field.
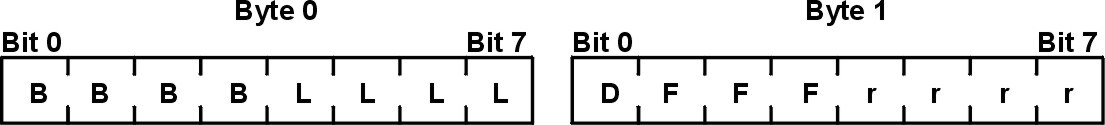
To find the routing control field value, use the iptrace daemon to look at incoming packets. Bits 1, 2, and 3 of Byte 1 are the Largest Frame Bits, which specify the maximum information field that can be transmitted between two communicating stations on a specific route. See the following for the format of the routing control field:
Figure 3-24. Routing Control Field. This illustration shows byte 0 and byte 1 of a routing control field. The eight bits of byte one are B, B, B, B, L, L, L, L. The eight bits of byte 1 are D, F, F, F, r, r, r, r.
 |
Values for the Largest Frame Bits
are as follows:
For example, if the maximum I-frame value is 2052 in the routing control field, the MTU size should be set to 2044. This is for token-ring network interfaces only.
Note: When using iptrace, the output file must not be on a Network File System (NFS).
If you cannot communicate with a remote host, try the following:
If you are having trouble with packet loss or are experiencing delays in packet delivery, try the following:
If you cannot communicate between a token-ring and an Ethernet network using a bridge, and you have verified that the bridge is good:
If snmpd is not responding to queries and there are no log messages received, the packet might be to large for the kernel User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet handler. If this is the case, increase the kernel variables, udp_sendspace and udp_recvspace by issuing the following commands:
no -o udp_sendspace=64000 no -o udp_recvspace=64000
The maximum size for a UPD packet is 64K. If your query is larger than 64K, it will be rejected. Split the packet into smaller packets to avoid this problem.
If you cannot get an IP address or other configuration parameters: