This task shows you how to enter the Surface Mesher workshop by:
-
Creating a new mesh part (using the Surface Mesher command)
Creating a Mesh Part
Open the Sample06.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
-
Select the geometry to be meshed.
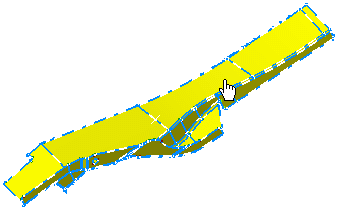
The Global Parameters dialog box appears.
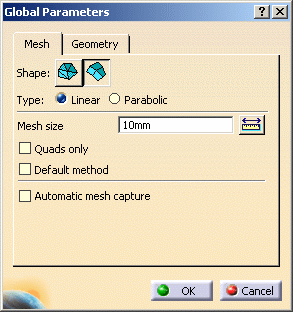
- Mesh tab: for more about this tab, click
here.
- Shape: lets you specify if you want to mesh the
surface with Triangle
 or
Quadrangle
or
Quadrangle
 elements.
elements. - Type: lets you specify if you want Linear or Parabolic elements.
- For more about the other options of this tab, refer to the
Mesh tab description.

The available options depend on the Shape option you selected.
- Shape: lets you specify if you want to mesh the
surface with Triangle
- Geometry tab: for more details about this tab, refer to the Geometry tab description.
Mesh tab
Triangle Method

- Mesh size: global size assigned to the mesh.
- Absolute sag: maximal gap between the mesh and the
geometry.
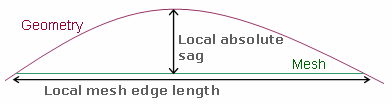
- Relative sag: is the ratio between the local
absolute sag and the local mesh edge length.
Relative sag value= (local Absolute sag value) / (local mesh edge length value)

-
Note that Absolute sag and Relative sag could modify the local mesh edge length value.
-
You can use both Absolute sag and Relative sag, the most constraining of the two values will be used.
- Min size: minimum value of the mesh size. Only available when you want to use Absolute sag or Relative sag.
-
- Automatic mesh capture: when activated, mesh capture
is performed dynamically on all the constraints (free edges,
internal edges, external edges) and after all constraints
modifications. You do not need to select all the constraints one
after the others.
Note that there is a capture tolerance, you can decide to impose or not a limitation to edge control neighborhood. Automatic capture is automatically performed using condensation. Meshing is then captured within the mesh part that belongs to the same CATAnalysis document, geometrically speaking.
Mesh can only be captured on updated mesh part.
- Tolerance: maximum distance for mesh capture.
- Mesh Part Selection
 : for
more details, refer to
Filtering Mesh Parts.
: for
more details, refer to
Filtering Mesh Parts.
Quadrangle Method

- Mesh size: global size assigned to the mesh.
- Quads only: lets you
generate automatically surface meshes with quads only when it is
possible (without
eliminating manually triangles).
If you select this check box, the Default method option is no more available.
-
To avoid triangle creation, the number of nodes must be even on each connected component of the boundary. However, if an odd number of nodes is imposed on one or several connected components (either by capture, nodes distribution specifications, or because all domains around are already meshed), the mesh may contain one or several triangles.
-
Selecting Quads only check box can lead to very bad meshes or even to invalid meshes near the boundary (for example: if this boundary contains acute angles, inhomogeneous distribution, ...), and in some cases, it can be impossible to create meshes.
-
- Default method: lets you choose a mesh method that
will be applied every time it is possible.
This option is not available if you selected the Quads only option.
If this option is selected, the Mesh size parameters will be ignored.
If this option is activated, you can choose between the following methods:
- Mapped free mesh: the mapped free mesh method will be applied.
- Minimal mesh: the minimal mesh method will be applied.
- Automatic mesh capture: when activated, mesh capture
is performed dynamically on all the constraints (free edges,
internal edges, external edges) and after all constraints
modifications. You do not need to select all the constraints one
after the others.
Note that there is a capture tolerance, you can decide to impose or not a limitation to edge control neighborhood. Automatic capture is automatically performed using condensation. Meshing is then captured within the mesh part that belongs to the same CATAnalysis document, geometrically speaking.
Mesh can only be captured on updated mesh part.
- Tolerance: maximum distance for mesh capture.
- Mesh Part Selection
 : for
more details, refer to
Filtering Mesh Parts.
: for
more details, refer to
Filtering Mesh Parts.
Geometry tab
- Constraint sag: constraint is created along the edge
of a face to avoid creating elements across this edge (the element
sag would be higher than the specified value). This does not
guarantee that the whole mesh respects the sag value but helps
creating constraints. For a given mesh size, the lower the
constraint sag value, the more numerous the constraints are
created, and vice versa.
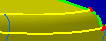
For example:
Due to the sag value (too high), the edges are not constrained (blue colored).


Due to the sag value (low enough), the edges are constrained (yellow colored).

- Constraints independent from mesh size: if this
option is deactivated, the Mesh size value will be the
reference value for the topological regrouping. If you activate
this option, you have to specify a reference value.
- Constraints ref size: lets you specify the
reference value.

- Use the same scale as the mesh size value.
- If you modify the reference value, the results could be unpredictable.
- Constraints ref size: lets you specify the
reference value.
- Add sharp edges: angle computed between two tangents on a contour.
- Min holes size: sets the diameter for automatic hole deletion
- Offset: value according to which both the geometrical simplification and meshing will be offset
- Automatic curve capture: if selected, this option
lets you find out all external curves located near the mesh part
geometric support (under a given geometric tolerance) and project
them automatically in order to create external constraints.
When performing automatic curve capture algorithm, projected geometries are chosen among the list of selected geometries. If the list is empty, projected geometries are chosen among all existing mesh parts geometric supports defined in the current analysis. In this case, the list is automatically updated with the geometries chosen for automatic curve capture.
Then each time you update the mesh part (due to design change for example), projected geometries will be only chosen among this list of authorized geometries.
This list is built only with updated geometries.
- Tolerance: maximum distance for curve capture.
- Geometry Selection
 : for
more details, refer to
Filtering Geometries.
: for
more details, refer to
Filtering Geometries.
- Mesh tab: for more about this tab, click
here.
-
Select the desired parameters in the Global Parameters dialog box.
-
Click OK.
The geometry appears as shown here:
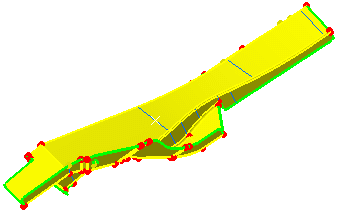
A Surface Mesh.2 object appears in the specification tree under the Nodes and Elements set.


You enter the Surface Mesher workshop.
You can now:-
Access the global parameters at any time.
-
Define local specifications of the surface mesher.
-
Launch the mesh execution.
-
Perform manually modifications.
-
Exit the Surface Mesher workshop at any time.
-
Editing an Existing Mesh Part
Open the Sample06.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
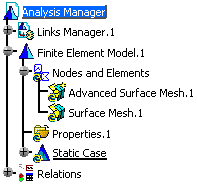
-
Update the Surface Mesh.1 mesh part.
This will launch the mesh execution.
-
Double-click the Surface Mesh.1 mesh part in the specification tree.
The Global Parameters dialog box appears.
For more details about this dialog box, click here. -
Click OK in the Global Parameters dialog box without any modification.

You enter the Surface Mesher workshop.
You can now:-
Access the global parameters at any time.
-
Define local specifications of the surface mesher.
-
Launch the mesh execution.
-
Perform manually modifications.
-
Exit the Surface Mesher workshop at any time.
-