
| MicroChannel Reference Database |
| Home | Adapters |
 |
|
| 8F6A ::: IBM Ethernet Quad-B2 PeerMaster 8F6D ::: IBM Ethernet Quad-BT PeerMaster | |
 | |
| Image courtesy of EPRM © IBM Corp. 1992-97 |
Adapter ID
Synopsis
Copyright Notice
Technical information and illustrations contained in this page are slightly edited excerpts from the EPRM, Copyright © IBM Corp. 1992-97. Adapter error coding schema explanation by MCA Base.
Features
The IBM Quad-BT and Quad-B2 PeerMaster Micro Channel Adapters provide the ability to connect a PS/2 MicroChannel server to four separate 10Mbps Ethernet LAN segments. Quad-BT refers to a 10Base-T adapter, Quad-B2 refers to a 10Base2 adapter.
These adapters:
Supported Systems
These adapters are Type 5 Micro Channel adapters. You can install them only in Type 5 adapter system-bus slots. Type 5 adapters are longer and wider than standard Micro Channel adapters. You can install Type 5 adapters in IBM PS/2 Models 85 and 95 and later-version PS/2 MicroChannel servers.
The PC Server Type 8641 (Models MZO, MZV, MZS, MZE, MZL) supports Type 5 Adapters in MicroChannel expansion slots 5 and 6, however, the adapter support bracket must be repositioned. If the server has been shipped with Peermaster adapter installed, the bracket has already been repositioned.
Operation Modes
• Traditional Adapter Mode
Used when you expect little or no cross-subnetwork traffic.
When the adapter is operating in this mode, the drivers for the adapter register each individual LAN segment with the network operating system (NOS) as a unique subnet. The NOS views the adapter as four separate adapters. Each network segment must be configured with a unique network number.
NOTE: Do not externally join (using bridges, switches, or concentrators) ports of adapters. You can configure as many nodes as you need, the adapter places no limit on the number of nodes per port. Ensure that each port is bound to the protocol with a unique network number.
• VNET Switch Mode
Used when you need to build subnets to provide cross-segment traffic.
When the adapter is operating in this mode, multiple LAN segments are registered with the NOS as a single subnet, called a VNET. VNETs are multisegment virtual subnets.
VNETs are made possible by a layer of virtual network software that binds to multiple instances of the adapter LAN driver and register them with the NOS as a single subnet. Multiple PeerMaster adapters may be configured to interoperate in various ways, such as:
All physical segments within a VNET are configured to the same network number. Cross-segment traffic within a VNET is switched by the adapter instead of by the server, allowing the server to be more productive.
External internetworking devices are not required to provide communication between segments with a VNET.
NOTE: Do not externally join (using briges, switches, or concentrators) ports of adapters that compromise a VNET. Nodes can be configured as needed, the adapter places no limit on the number of nodes per port. Ensure that all ports in a VNET are bound to the protocol (by way of VNET) with a common network number.
Configuration Examples
• Traditional Adapter Mode
An 8-port network with two PeerMaster adapters configured in the Traditional Adapter mode:
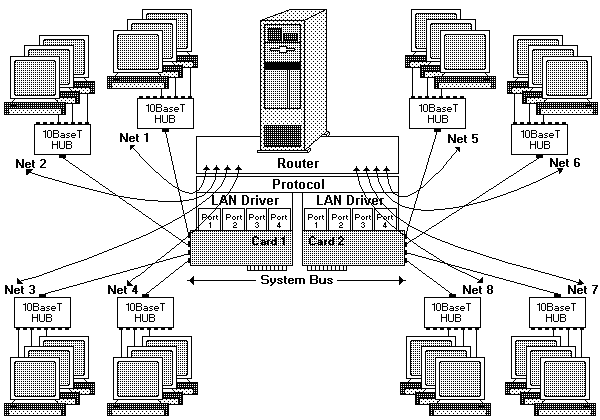
NOTE: The same principles apply to Quad-B2 configurations, however concentrator hubs are not required for 10Base2 operation.
This illustration shows:
Software layers illustrated above the adapters indicating software that is required to route traffic internally, running on the server.
Cross-subnet traffic, such as traffic from Net 1 to Net 2 , must be forwarded by a router. The router can be internal to the server or an external stand-alone device.
The advantage of the Traditional Adapter mode is that a router restricts cross-subnet traffic to only those data packets that are uniquely addressed to the target network. The disadvantage of this mode is that server responsiveness might be heavily impaired due to the burden of packet routing. This mode should be used only when little or no cross-subnet traffic is expected.
• VNET Switch Mode - Single VNET
The illustration below shows two Quad-BT PeerMaster adapters (Card 1 and Card 2) forming a single VNET:
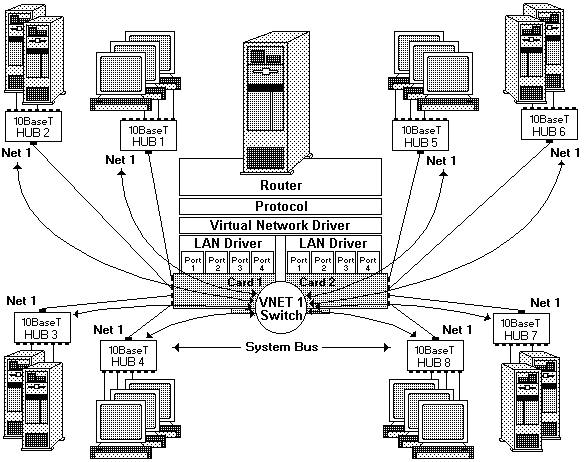
NOTE: The same principles apply to Quad-B2 configurations, however concentrator hubs are not required for 10Base2 operation.
The adapter provides the function of a high-performance network adapter combined with the power of an Ethernet switching hub.
• All segments configured as Network number 1 (Net 1).
• Curved arrows indicating the flow of data across ports connected by the VNET switch.
The VNET switch performs all cross-segment traffic, and, therefore, server responsiveness is not impaired by heavy cross-segment traffic. The adapters perform two types of frame switching: port-to-port and peer-to-peer.
• VNET Switch Mode - Multiple VNETs
The illustration below, a configuration of two network numbers (Net 1 and Net 2), shows an 8-port network with two Quad-BT PeerMaster adapters (Card 1 and Card 2) each configured as an independent VNET (two VNETs),

NOTE: The same principles apply to Quad-B2 configurations, however concentrator hubs are not required for 10Base2 operation.
The curved arrow that passes through the LAN drivers, protocol stacks, and router in the server represents the connection between the two subnets (Net 1 and Net 2). Cross-subnet traffic, such as traffic from Net 1 to Net 2, must be forwarded by a router. The router can be internal to the server or an external stand-alone device.
Each VNET may represent a separate department or workgroup. The four switched ports within each VNET provide a multisegment workgroup environment. Isolating the two VNETs by a way of the server-based router allows you to create a seperation between two departments. You can configure the router to permit restricted traffic to pass between the departments.
• VNET Switch Mode - - Combined VNETs and Traditional Nets
The illustration below, a network using PeerMaster adapters, shows a five-subnet network (Net 1, Net 2, Net 3, Net 4, and Net 5) configured as one four-segment VNET (VNET 1) on Card 1 and four traditional networks on Card 2. Use this configuration only when you expect little or no cross-VNET traffic:
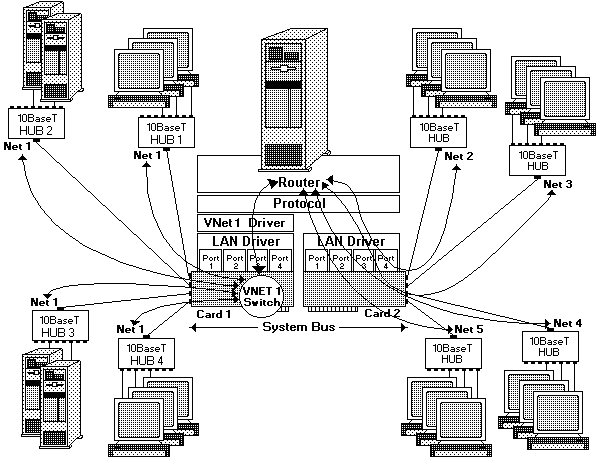
NOTE: The same principles apply to Quad-B2 configurations, however, hubs are not required for 10Base2 operation.
Cross-subnet traffic, such as traffic from Net 1 to Net 2, must be forwarded by a router. The router can be internal to the server or an external stand-alone device.
This VNET may represent a large department while the traditional networks may represent small workgroups. You can configure the router to restrict traffic between departments.
Cabling for 10Base-T Networks
Two types of network cables may be connected to the Quad-BT PeerMaster adapter: straight-through and crossover.
• Straight-Through
Use straight-through cables when connecting your adapter to an external 10Base-T concentrator hub.

• Crossover
Use crossover cables to directly connect your adapter to another 10Base-T device, such as a workstation, server, or another adapter. Crossover cables create dedicated segments. A dedicated segment is two point-to-point devices connected to a dedicated link.
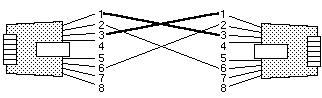
Ensure that you do not externally join ports of adapters (using bridges, switches, or concentrators).
Cabling for 10Base2 Networks
To connect any port of the Quad-B2 PeerMaster adapter to a 10Base2 thin Ethernet cable segment - a thin Ethernet cable segment is the length of the cable between the repeaters - do the following:
NOTE:
Symptom-to-FRU Index
The Symptom-to-FRU index contains the following diagnostic information:
If you receive an error that is not described in the preceding error-message lists, you might have an unrecoverable (fatal) error. The error message indicates that the adapter has experienced an unrecoverable run-time error.
To make the adapter functional, unload the drivers, then reload them. If unloading and reloading the drivers does not make the adapter functional, restart the computer and try again.
If the above procedures do not correct the problem, replace the 10Base-T or 10Base2 adapter.
• LED Indications
NOTE: The PeerMaster adapter LED is normally off prior to adapter download, and is normally on after successful download.
REASON: DRAM failure. DRAM memory stick may be missing or loose
ACTION: Insert or reseat memory and try again
REASON: POST Failure
ACTION: Run the adapter diagnostic to get the exact error and recommended action.
REASON: Flash Checksum Failure
ACTION: Replace Flash with programmed part.
• Adapter Error Codes
The error codes for the 10Base-T and 10Base-2 adapters are encoded by the following simple schema (Ed: This is not described or explained in the EPRM):
027 X nn S0
An error code is represented by a 6-digit number 027Xnn followed by a S0. The X in 027X designates the adapter where 6 resp. 0276 indicates the 10Base-T adapter and 7 resp. 0277 indicates the 10Base-2 adapter. The next two digits nn are the actual error codes: 01, 02, ... 33 and 91, 92, 93, 99.
| X=6 : 10Base-T X=7 : 10Base-2 | SYMPTOM | FRU / ACTION |
| 027X01S0 027X02S0 027X03S0 027X04S0 | POST Flash Main Sector Checksum Failure | Adapter |
| 027X05S0 027X06S0 027X07S0 027X08S0 027X09S0 027X10S0 027X11S0 027X12S0 | Verify proper seating of the DRAM SIMM on the adapter | Adapter |
| 027X13S0 027X14S0 027X15S0 027X16S0 027X17S0 027X18S0 027X19S0 027X20S0 | POST SRAM failure | Adapter |
| 027X21S0 027X22S0 027X23S0 027X24S0 027X25S0 | -- | Adapter |
| 027X26S0 | POST Ethernet Port 1 External Loopback Failure | - Verify correct cabling of Port 1 - Adapter |
| 027X27S0 | POST Ethernet Port 2 External Loopback Failure | - Verify correct cabling of Port 2 - Adapter |
| 027X28S0 | POST Ethernet Port 3 External Loopback Failure | - Verify correct cabling of Port 3 - Adapter |
| 027X29S0 | POST Ethernet Port 4 External Loopback Failure | - Verify correct cabling of Port 4 - Adapter |
| 027X30S0 027X31S0 027X32S0 027X33S0 | -- | Adapter |
| 027X91S0 027X92S0 027X93S0 027X99S0 | -- | - Run Setup and verify the adapter configuration - Adapter |
• NetWare load-time error messages
Not listed here. Consult EPRM or contact MCA Base.
• NetWare run-time messages
Not listed here. Consult EPRM or contact MCA Base.
Drivers
Network Operating System Requirements
Use one of the following network operating systems:
Option Diskette
The PeerMaster Server Adapter Option Diskette is shipped with the PeerMaster Server Adapter options. The diskette contains the following:
Links
The adapter page of the IBM Ethernet Quad-B2 PeerMaster Adapter.
The adapter page of the IBM Ethernet Quad-BT PeerMaster Adapter.
For additional information and Quad-B2/BT PeerMaster resources see www.gilanet.com/ohlandl/NIC/Peermaster.html
ADF Adapter Description File
@8F6A.ADF IBM Ethernet Quad-B2 PeerMaster
@8F6D.ADF IBM Ethernet Quad-BT PeerMaster
| Legal | Copyright | top |