Defining the Report Format
|
|
You use this
function, together with the function described in Generating a Report, to
get the values of properties of objects in a document. You can also get
related information, such as number of objects. This task shows you
how to define the report format.
Examples from the Piping workbench are used here. Substitute the appropriate resource or directory when working in another workbench. |
|
|
|
Before you generate a
report you need to define its format. This means deciding which properties
you are interested in. This report format is kept in a file which you can
use to generate reports from other documents.
It is recommended that you use queries, as explained below, if you will be modifying a document and running a report on it repeatedly. To use this function you must first make sure of a setting. Click Tools - Options - General - Parameters and Measure and click on the Knowledge Environment tab. Under Language check Load extended language libraries. Either check All Packages, or uncheck this option and load the packages you will be using. |
|
|
|
1. | Click Tools - Report -
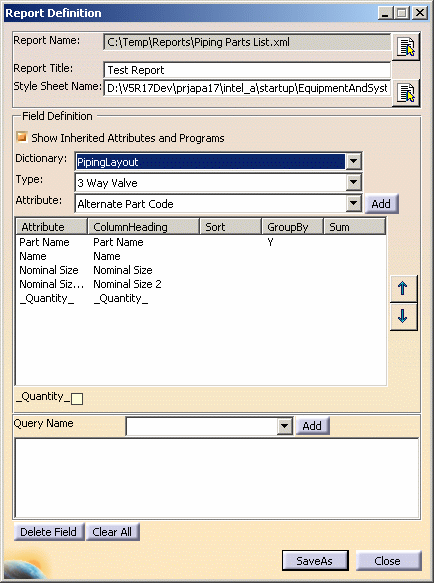
Define. The Report Definition dialog box displays.
You can toggle between Yes and No for the Column headings Sort, GroupBy and Sum. A blank means No. To toggle click beneath the column heading. In the example above, for the attribute Name, Sort is No, GroupBy is Yes and Sum is No. The Up and Down arrows on the right allow you to change the position of the attribute in the pane. To use, select an attribute and click an arrow. |
| 2. | The report name field is informative. You can use the button next to it to open an existing report. You will need to enter a report name and location when you click the Save As button. Enter a report title - you can enter anything but you must have a title. | |
| 3. | Select a style sheet by clicking
on the button next to the Style Sheet Name field. You can use
sample style sheets provided with this application, modify the samples,
or create your own. NOTE: If you want to use style sheets to
change the looks or format of your generated report, then the report
must be saved in XML format.
You can reference three sample style sheets that are provided with this application to make the output file easier to read. One of the three style sheets also allows you to sort. The style sheets are located in the directory ...intel_a\startup\Equipmentand Systems\ReporterData.
If style sheet information has not been selected in your report format - for instance in formats created using early releases - you can add it to existing reports using the following procedure:
|
|
| 4. | Check the Show Inherited Attributes box if you want to. | |
| 5. | Click on the down arrow next to the Dictionary field and select the dictionary related to your program. In this case the PipingLayout package has been selected. See Using Knowledgeware Packages for more information. | |
| 6. | Select the type of object by clicking the down arrow next to the Type field. The list of attributes you will see in Step 6 will depend on the type you select here. However, when you generate a report you will get values for all objects in the document that have the attributes included in your report format. If you want to limit the objects for which you get a report you must create a query (Step 8). | |
| 7. | Select an attribute in the Attribute field and click the Add button. The attribute will be added in the window. Add as many attributes as you want to by repeating the process - attributes are added one at a time. | |
| 8. | Select Yes or No for the column
headings.
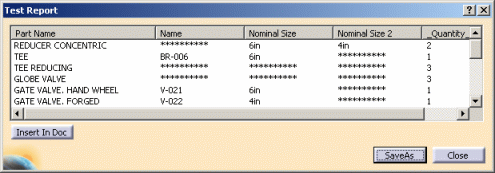
If the objects you group have attributes that have unique values, then the values will be replaced by asterisks. For instance, Globe Valves in the report above, have three unique names, therefore the Name field shows asterisks. |
|
| 9. |
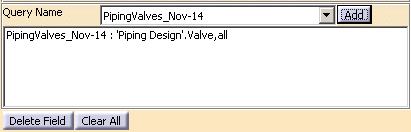
To use a query you have already defined, click the down arrow next to the
Query Name field and select it. Click the Add
button to display it in the pane. There is more explanation about
queries below.
You can further refine your report by using the Edit - Search function to define a query. This will allow you to generate a report on a narrower selection of check valve, say, of a certain size, instead of all check valves in your document. The queries you create will be available for selection when you click the arrow in the Query Name field above. Detailed instructions on using the Search function can be found in the Infrastructure User Guide under Basic Tasks - Selecting Objects. Briefly, click Edit - Search to bring up the Search dialog box. Select the Advanced tab, then select a workbench, type of object and attribute you are interested in. Clicking the Add to Favorites button brings up the Create a Favorite Query dialog box, where you can name the query and save it. |
|
| 10. | Use the Delete Field button to clear any of the entries, Clear All to remove all, SaveAs to save, and Close to exit the command. | |
![]()