This task
shows you how to create a symmetric mesh part from a parent mesh part.
This transformation is available in case of 1D, 2D and 3D mesh parts.
Open the Sample40.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
- To create a 1D or 2D transformed mesh part, the FEM Surface (FMS) product is required.
- To create a 3D transformed mesh part, the FEM Solid (FMD) product is required.
- All the mesh parts must have been updated before creating a translation mesh part.
-
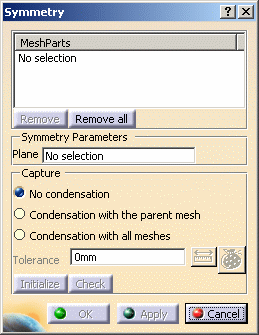
Click Symmetry Mesher
 in the Mesh Transformations toolbar.
in the Mesh Transformations toolbar. -
Select the Advanced Surface Mesh.2 mesh part.
-
Select the zx plane in the specification tree.
-
Click No condensation.
-
Click Apply and then OK.
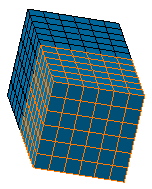
A Symmetry Mesh.1 mesh part appears in the specification tree and the symmetric mesh part is created.

For a better visualization, select the Symmetry Mesh.1 object in the specification tree.
-
To do this,
-
Click Intersections / Interferences
 in the Mesh Analysis Tools toolbar.
in the Mesh Analysis Tools toolbar. -
Enter 0.001 mm as Clearance value and click Apply.
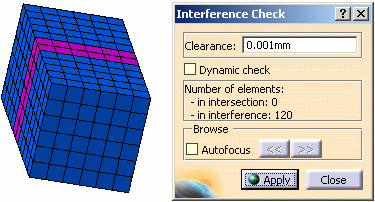
You can see that there are 120 elements in interference because the nodes of the symmetric mesh part and the parent mesh part have not been condensed.
-
Click Close.
-
-
Edit the symmetric mesh.
To do this, double-click the Symmetry Mesh.1 object in the specification tree.
The Symmetry dialog box appears. -
Click Condensation with the parent mesh.
-
Enter 1mm as Tolerance value.
-
Click Apply and the OK.
The symmetric mesh seems to be identical to the previous one.
-
Check the intersections.
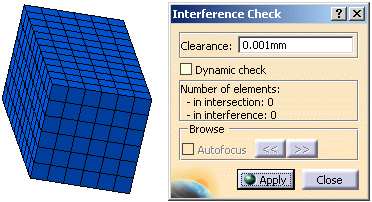
In this case, there is no element in interference because the nodes of the symmetric mesh part and the nodes of the parent mesh part have been condensed.
-
Click Close in the Interference Check dialog box.
![]()