This task shows how to create a Pressure applied to surface geometry.
Pressures are intensive loads representing uniform scalar pressure fields applied to surface geometries, and characterized by the fact that the force direction is everywhere normal to the surface.
Pressure objects belong to Loads
sets.
Units are pressure units (typically N/m2 in SI).
Pressures can be applied to the following types of supports:
|
Geometrical Feature |
Mechanical Feature |
Analysis Feature |
||||
|
Spatial Groups |
Geometrical Groups |
Groups by Neighborhood |
Groups by Boundary |
Others |
||
|
Face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
To know more, refer to Authorized Supports.
Open the sample00.CATAnalysis document from the samples directory.
-
Go to View > Render Style > Customize View and make sure the Shading, Outlines and Materials options are active in the Custom View Modes dialog box.
-
Click Pressure
 in the Loads toolbar.
in the Loads toolbar.The Pressure dialog box appears.
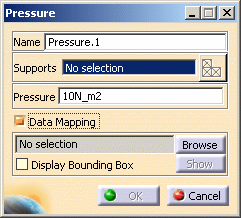
-
Name: lets you modify the name of the pressure.
-
Supports: lets you select the support on which you want to apply the pressure.
-
Pressure: lets you enter the value of the pressure you want to apply.
A positive value describes a pressure whose resultant is directed towards the material side of the selected surface. -
Data Mapping: lets you use the data mapping functionality.
For more details about the Data Mapping functionality and data mapping files, refer to Data Mapping in the Frequently Asked Questions section.
The data mapping option is only available with the ELFINI Structural Analysis (EST) product.
-
-
You can change the identifier of the Pressure by editing the Name field.
-
Enter the value of the scalar pressure. A positive value describes a pressure whose resultant is directed towards the material side of the selected surface.
-
Select the Data Mapping check box.
-
Click the Browse button in the Pressure dialog box and load the desired external file. Make sure the file type is actually *.txt.
The File Browser dialog box lets you select the desired file.
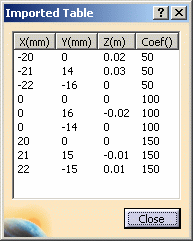
In this particular example, select the MappingFileExample.txt file in the samples directory.When you click Open, the Pressure dialog box is updated.
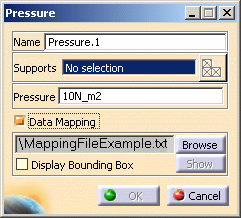
The Show button now lets you visualize the imported file inside the session. If you then modify the pointed file, the values are synchronized and the load feature invalidated.
-
Select the geometry support (a face) on which you want to apply the Pressure. Any selectable geometry is highlighted when you pass the cursor over it.
You can select several supports in sequence, to apply the Pressure to all supports simultaneously.
Several arrows symbolizing the pressure are visualized.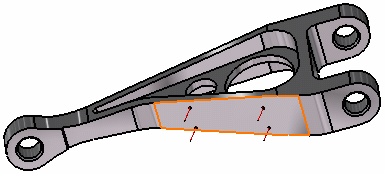
As soon as the support is selected, the Select Mesh Part button is available.
To know more about the Select Mesh Part button, refer to Selecting Mesh Parts. -
Click OK in the Pressure dialog box.
A Pressure object appears in the specification tree under the active Loads objects set.
- You can either select the surface and then set the pressure value, or set the pressure value and then select the surface.
- If you select other surfaces, you can create as many Pressure Loads as desired with the same dialog box. A series of Pressures can therefore be created quickly.
- Loads are required for Stress Analysis computations.
- If several Analysis Cases have been defined in the Finite Element Model, you must activate a Loads objects set in the features tree before creating a Pressure object (only available if you have ELFINI Structural Analysis (EST) product installed).
- Pressure objects can be edited by a double-click on the corresponding object in the specification tree.
Make sure the computation is finished before starting any of the following operations.
The ELFINI Structural Analysis product offers the following additional functionalities:
-
Contextual menu on the load object:
- Pressure visualization on mesh: the translation of pressure specifications into solver
specifications can be visualized symbolically at the impacted mesh
elements, provided the mesh has been previously generated using a mesh
only computation.
To know more, refer to Visualizing Loads on Mesh.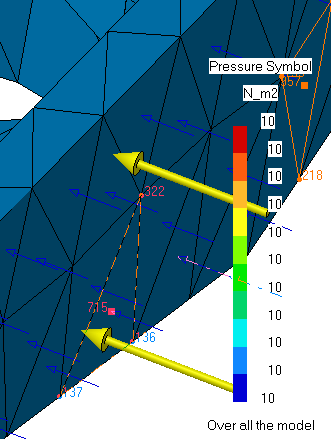
- Pressure visualization on mesh: the translation of pressure specifications into solver
specifications can be visualized symbolically at the impacted mesh
elements, provided the mesh has been previously generated using a mesh
only computation.
-
Contextual menus on the Loads set:
- Generate Image: generates an image of the computed load
objects (along with translating all user-defined Loads specs into
explicit solver commands on mesh entities), by generating symbols for
the elementary loads imposed by the Loads set. The image can be
edited to include part or all of the options available.
Right-click Loads.1 in the specification tree and select Generate Image.
The Image Generation dialog box appears.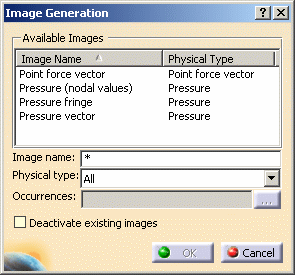
To know more, refer to Generating Images.
- Report: the partial status and results of intermediate
pre-processor computations are reported in HTML format. It represents a
subset of the global report capability and generates a partial report
of the Loads set computation.
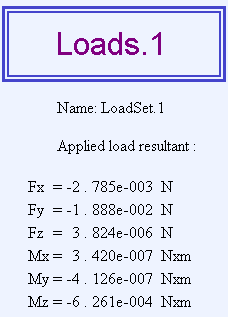
To know more, refer to Generating Reports.
- Generate Image: generates an image of the computed load
objects (along with translating all user-defined Loads specs into
explicit solver commands on mesh entities), by generating symbols for
the elementary loads imposed by the Loads set. The image can be
edited to include part or all of the options available.
-
Self balancing on Loads set:
already named Inertia Relief.
Double-click Loads.1. The Loads dialog box appears:
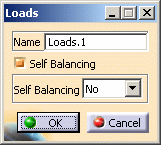
The Loads dialog box lets you choose whether you wish to apply self-balancing to the load. If activated, this option automatically adds inertia forces in order to counter balance external loads. Thus the global loading equals null.
This kind of loading is used when modeling free bodies submitted to constant external forces (for example: a rocket during lift-off).This option is usually combined with iso-static restraint.
In this case, reaction forces are null, which simulates a free body.
![]()