- Raster
- CGM (described in "Configuring an Existing Printer")
- PostScript
- HPGL
- HPGL2
- HP DesignJet 1000 Series
- HP DesignJet 4000 Series
- SVG
- EMF.
Select File > Printer setup... to open the Printers dialog box:
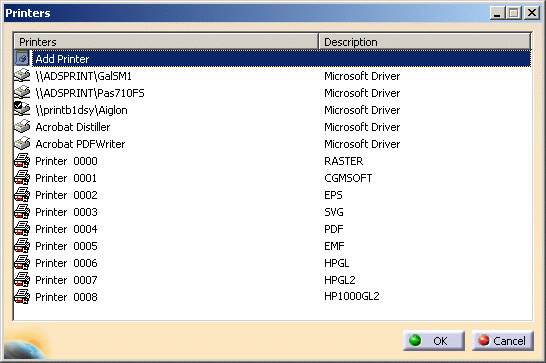
- by selecting Start > Programs > CATIA > Tools > Printers V5Rn
where "n" is the current release number
- by accessing the directory
/usr/Dassault Systemes/B0n(on UNIX) orC:\Program Files\Dassault Systemes\B0n\intel_a\code\bin(on Windows) then entering
CATPrinterManagerwhere "n" is the current release number
Scenario 1: Raster
-
Right-click the Raster printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the
Printer Properties dialog box.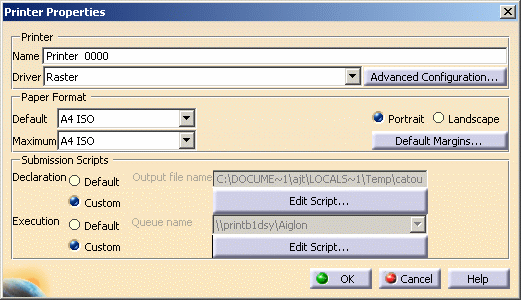
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
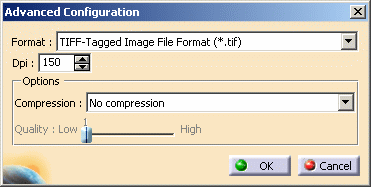
-
Select the format to be used from the Format list: TIFF, BMP, JPEG, WMF, etc.
You can also set more precisely the desired DPI value using the Dpi box. -
In the Options area, select the compression type:
-
No compression
-
Packbits
-
JPEG
-
HUFFMAN
-
Fax Group 4.
If you choose the JPEG type, the Quality slider is activated to let you specify the compression quality: the higher the rate,
the better the quality. -
-
When finished, click OK to validate and close the Advanced Configuration dialog box.
Scenario 2: PDF
Scenario 3: PostScript
-
Right-click the PostScript printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the
Printer Properties dialog box.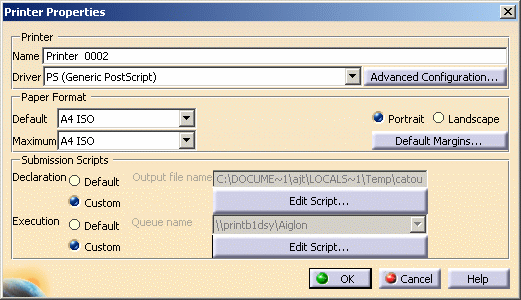
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
-
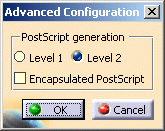
Choose the level for PostScript generation by selecting the appropriate option: Level 1 or Level 2.
-
If you want to use the EPS format, select the Encapsulated PostScript check box. EPS does not contain page description
directives and is designed for portable exchange between applications and platforms. It may also be included in a larger
PostScript document. -
Click OK to validate.
Scenario 4: HPGL
-
Right-click the HPGL printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the
Printer Properties dialog box.
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
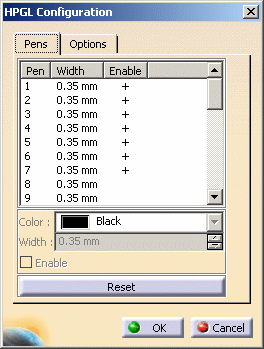
The Pens tab lets you create a mapping between the original Version 5 document and the result in HPGL format by defining the width and color to be applied to pens that will be used. Each of the pens is associated to a color (RGB) and a thickness (in millimeters).
To do so, the pens to be used are selected using the following priority order:
-
first, by their color in order to use a color matching (exactly or as close as possible) the one of the original document
-
then, by their width. The width that is used corresponds either to the real width (i.e. as defined in the model) of the element to be drawn or to the width of the pen, depending on the option you activate for Thickness Printing.
The goal of this capability is to have the printing that best suits your device specifications with respect to the limitations inherent in HPGL printer language. Note that the smallest units that can be supported by HPGL are 40 units per millimeter (1016 per inch). As the accuracy cannot exceed this value, discrepancies might occur when comparing documents (32-bit/64-bit, for instance).
-
-
Select a pen from the list.
As soon as a pen is selected, the other fields displayed below are activated and you can then specify the color and the width to be applied to the selected pen.
By default, each pen you select is already assigned a color and a width but you can modify them as needed using the Color list and the Width box. -
Select the Enable check box if you want the selected pen to be used when printing. When a pen is active, it is identified by a
"+" sign in the Enable column.
If you are not satisfied with the parameters you defined, you can click Reset to recover the original parameters. -
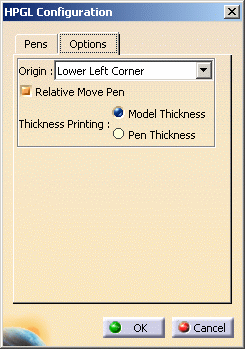
Access the Options tab:
-
Indicate the location at which the pen will start using the Origin list:
-
Click OK to validate and close the HPGL Configuration dialog box.
Scenario 5: HPGL2
-
Right-click the HPGL2 printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the
Printer Properties dialog box.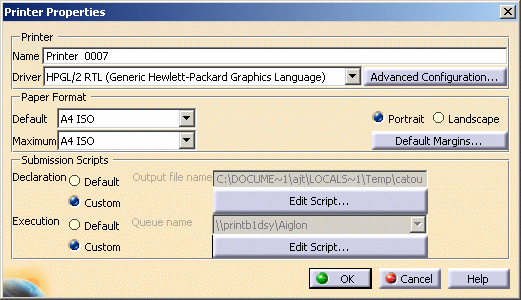
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
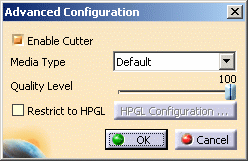
The Enable Cutter check box is selected by default and means that the media is cut after printing. -
Select the desired Media Type (i.e. the type of paper to be used) from the list: paper, polyester film, etc.
-
Define the Quality Level using the slider.
-
Select the Restrict to HPGL check box if you want to use the printer for HPGL data only.
Activating this option also activates HPGL Configuration... which lets you access the HPGL Configuration dialog box.
-
When finished, click OK to validate.
Scenario 6: HP DesignJet 1000 Series
-
Right-click the HP DesignJet 1000 Series printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name)
to access the Printer Properties dialog box.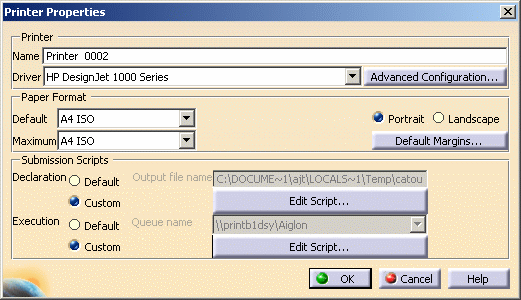
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
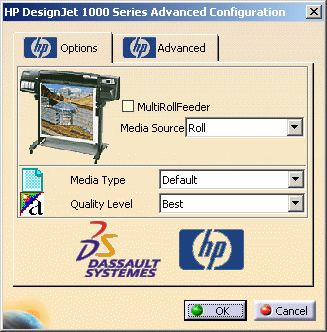
In the Options tab, you need to:
-
Specify how the printer will be loaded using the Media Source list: Roll or Manual feed.
For printers with an integrated multi-roll feeder, you also need to select the MultiRollFeeder check box ption to specify the roll to be used: to do so, select the desired roll number from the Media Source list, i.e. "Roll 1", "Roll 2", etc.
-
Use the Media Type list to indicate the type of media to be used: paper, vellum, polyester film, etc.
-
Select the Quality Level to be used: Fast, Normal or Best. By default, Best is selected.
-
Access the Advanced tab:

-
By default, all the options displayed are selected but you can deactivate them if needed:
-
Line Sharpening (RET) enhances detail in line drawing. It is especially useful for drawings with a lot of details
-
Enable Cutter activates the cutter mechanism which cuts the media after printing
-
Inked Area takes the first object encountered in the plot and places that object at the origin (0,0 coordinate). After the last object is printed, the printer adds the margin and the plot is complete. When this option is activated, white area around the plot, as well as page size information coming from the software is ignored.
This option is recommended when using roll media and when centering is not important. This option also provides optimal paper usage -
Autorotate lets the printer decide at print time which orientation requires the least media for your drawing based on the "roll media" that is loaded.
-
-
When finished, click OK to validate.
Scenario 7: HP DesignJet 4000 Series
dedicated driver.
HP DesignJet 4000 Series printers allow you to rapidly produce higher-quality large-format prints, addressing demand for improved
printing precision, especially for technical drawings. You also benefit from having full UNIX-Windows compatibility and the same
functional level on both platforms.
For detailed information, you can browse the HP Internet site:
http://www.hp.com
-
Right-click the HP DesignJet 4000 Series printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the Printer Properties dialog box.
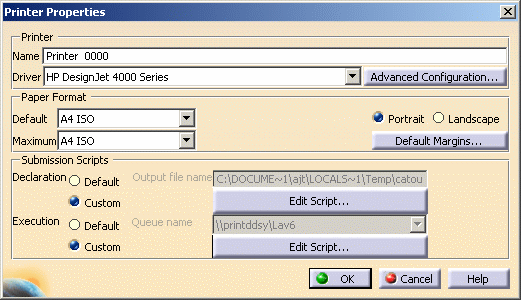
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
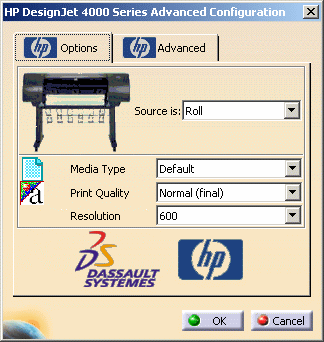
In the Options tab, you need to:
-
Specify how the printer is loaded using the Source is list: Roll or Manual feed.
-
Use the Media Type list to indicate the type of media to be used: paper, vellum, polyester film, etc.
-
Select the Print Quality to be used: Fast (draft), Normal (final) or Best (enhanced). By default, Normal (final) is selected.
-
Indicate the Resolution to be applied: either 300, 600 or 1200. By default, "600" is selected.
-
Access the Advanced tab:

-
By default, some options are selected but you can deactivate them if needed:
-
Optimize for Drawings/Text enhances detail in line drawing. It is especially useful for drawings with a lot of details
-
Maximum Detail enables to view as much detail as possible by increasing both the printing and rendering resolution
-
Disable Automatic Cutter deactivates the cutter mechanism which cuts the media after printing
-
Remove Top/Bottom Blank Areas takes the first object encountered in the plot and places that object at the origin (0,0 coordinate). After the last object is printed, the printer adds the margin and the plot is complete. When this option is selected, white area around the plot, as well as page size information coming from the software is ignored.
This option is recommended when using roll media and when centering is not important. This option also provides optimal paper usage -
Autorotate lets the printer decide at print time which orientation requires the least media for your drawing based on the "roll media" that is loaded.
-
-
When finished, click OK to validate.
Scenario 8: SVG
-
Right-click the SVG printer in the list then select Configure (or double-click the printer name) to access the
Printer Properties dialog box.
-
Click Advanced Configuration....
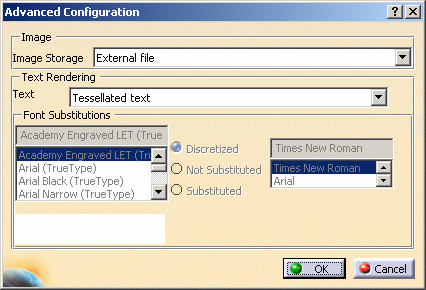
-
Use the Image Storage list to indicate if you want the image to be stored in an external JPEG file
(with links to the SVG file) or to be embedded in the SVG document. -
The Text list lets you specify whether the text should be rendered as a tessellated text or using system fonts:
-
selecting Tesselated text means that all glyphs will be displayed as polygons. If you choose this option, skip the next step
-
selecting Use system font lets you replace the font of your choice by another one.
-
-
If you selected Use system font in the Text list, the Font Substitutions area is activated to let you replace the font of your
choice by another one. To do so, first select a font in the list displayed to the left then select the appropriate option:-
Discretized: means that when the image suffers from a lack of points, points are distributed to fill the gaps and ensure linearity
-
Not Substituted: means that the selected is not replaced by another font, it is kept as is
-
Substituted: means that the selected font is replaced by a suitable replacement font you select in the list displayed to the right. This list is activated as soon as the Substituted option is selected.
-
-
When finished, click OK to validate.