- General STEP options:
- Import STEP options:
- Export STEP options:
General
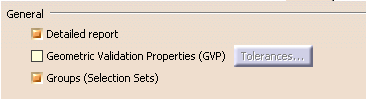
Detailed report
By default, the report file contains a Detailed Conversion chapter. Click to clear the Detailed Report option to remove this chapter from the report file.
Geometric Validation Properties (GVP)
This functionality is available in STEP AP214 and AP203 ed2, i.e. Geometric Validation Properties are attached at product level, according to Recommended Practices for Geometric Validation Properties 2nd Extension March 24, 2006
When the Geometric Validation Properties
option is selected, the Tolerances button becomes available.
It
opens a dialog box where you can define the tolerances for the GVP checking.
The dialog box looks like this if you have selected Standard Scale:
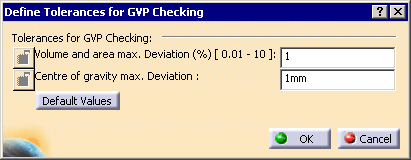
- The first tolerance is the percentage of variation of volume or area allowed. Default value: 1%.
- The second tolerance is the maximum error for the center of gravity.
Default value: 1mm for the Standard Scale and - Click Default Values to revert to the default values (1 and 1mm or).
For import:
- Geometric validation properties are computed for each solid, shell, product or instance, and this information is written in the report file.
- For each solid, shell, product or instance, the report file gives the computed geometric validation properties:
- Centroid: coordinates of the center of gravity (applies to solid, shell, product or instance),
- Area: area of the entity (wetted area for solids) (applies to solid, shell or product),
- Volume: volume of the entity (for solids only) (applies to solid or product).
- If the imported STEP file contains geometric validation properties, these properties are read. This information is written in the report file.
- For each read geometric validation properties, the report file gives the status of comparison between read and computed properties, with the following information:
- Centroid deviation error (distance measure) (applies to solid, shell, product or instance),
- Surface area difference value and error ratio (applies to solid, shell or product),
- Volume difference value and error ratio (applies to solid or product).
- A global status for the conversion is given, together with the maximum deviations found.
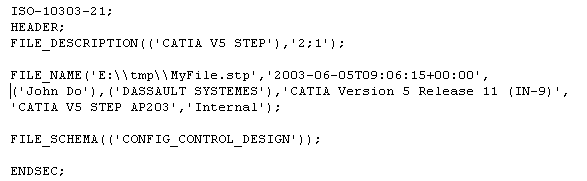
Example of a report file:

- ratios (Volume difference and Surface area difference) are lower than 1%.
- and the centroid deviation is lower than 1 mm.
If all status are ok, the global status is ok too.
The maximum deviation found for each comparison (centroid, area and
volume) is given in the report file with the corresponding entities (the
maximum deviations found do not necessarily apply to a single object).
This functionality involves a slight performance loss, due to the
properties computation cost.
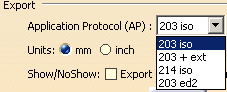
For export:
- The exported STEP file includes geometric validation properties for each solid, shell, product or instance, according to STEP AP214 and AP203 ed2 and the CAX-IF recommended practices.
- For each solid, shell, product or instance, the report file gives the computed geometric validation properties:
- Centroid: coordinates of the center of gravity (applies to solid, shell, product or instance),
- Area: area of the entity (wetted area for solids) (applies to solid, shell or product),
- Volume: volume of the entity (for solids only) (applies to solid or product).

If the option Assemblies/Structure only is selected, the Geometric Validation Properties are not available.
This functionality involves a slight performance loss, due to the properties computation cost.
Groups (Selection Sets)

By default, this option is selected:
- at import, Groups found in the STEP file are translated into Selection Sets.
- at export, Selection Sets found in the CATIA file are exported as Groups in the STEP file. Refer to the STEP: Export chapter for more information (Miscellaneous section).
However, importing or exporting Groups may be time consuming. Click to clear this option and de-activate the processing of Groups.
Import
Continuity optimization of curves and surfaces

This setting allows a better user control over the number of
curves and surfaces that are created during the process of importing STEP
data into V5:
V5 requires its geometry to be C2-continuous. When non C2-continuous
geometry must be imported from a STEP file, this geometry (curves, surfaces)
is broken down into a set of contiguous geometries, each of them being
C2-continuous. This is what happens when the No Optimization option is
chosen.
However, this can produce an increase of the size of the resulting data,
because more curves/surfaces are created. In order to limit this drawback,
two other modes are optionally offered.
In those modes, the STEP interface tries to limit the splitting of curves
and surfaces by modifying their shape slightly, so that they become
C2-continuous while remaining very close to their original shape.
In order to guarantee that the deformation is not excessive, a maximum
deviation parameter is used. When in Automatic optimization
mode, this maximum deviation is read into the STEP file itself, in the STEP
parameter that documents the precision of points in the file. In this mode,
the value read from the STEP file is then corrected so that it remains
comprised between 10E-2 and 10E-3. This guarantees an optimization that
remains compatible with the precision for the data that was set by the
emitting system.
Last, if this strategy is not enough, you can choose the Advanced
optimization mode, in which an arbitrary deviation value can be
entered.
You can find useful information in the report file. Please see the Report file section in the STEP Import chapter in this User's Guide.
The Automatic optimization proposes:
- No approximation, thus this option does not create a significant deformation and keeps the internal BSpline structure (equations and knots).
- A continuity optimization is performed within the deformation tolerance used for optimizing BSplines, comprised between 0.001mm and 0.01mm (depending on the tolerance value defined within the imported STEP file) on:
- BSpline surfaces,
- BSpline boundary curves (3D and P-curves when available),
- BSpline independent 3D curves,
- The parameters box cannot be activated
This option softens the effect C2 cutting of faces and boundaries (which is mandatory in V5) without any significant geometric deformation
If you select No optimization:
- No optimization is performed on BSplines (neither curves nor surfaces).
- Elements are cut at discontinuity points to suit the modeler (exact mathematic continuity). This may result in a dramatic number of faces and boundary curves, data of poor quality and poor performances in further use in V5.
If you select Advanced optimization:
- No approximation. The internal BSpline structure (equations and knots) is kept,
- A continuity optimization is performed on:
- BSpline surfaces,
- BSpline boundary curves (3D and P-curves when available),
- BSpline independent 3D curves,
- but the deformation tolerance is set by the user (see Parameters).
With this option, you can enter a larger tolerance value which may enhance the optimization impact (resulting in less C2 cutting on faces).
Click Parameters to
access advanced optimization options and tolerances.
The dialog box looks like this if you have selected Standard Scale:
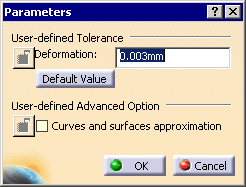
Note that the tolerance is shared by the optimization
process (in all cases), the Curves and surfaces approximation and the
Topological reduction of boundaries if you have selected those check boxes.
For example, you have a deformation tolerance of 0.001mm and
you have selected Curves and surfaces approximation.
The tolerance for the optimization will be 50%, i.e. 0.0005mm and that of
the Curves and surfaces approximation will also be 50%.
Thus, the number of cuts of the faces will vary according to
the value entered, and according to the number of check boxes selected.
-
Deformation: maximum deformation (in millimeter) allowed in the optimization of curves and surfaces:
- For the Standard Scale, it ranges between 0.0005 and 0.1 mm. The default deformation is 0.003mm.
- For the Small Scale, it ranges between 5e-006 mm and 0.001 mm. The default deformation is 3e-005mm.
Click Default Value to revert to the default value.
User-defined Advanced Option: Curves and surfaces approximation:
- By default, this option is not selected.
- BSpline surfaces and curves continuity is optimized,
- In addition, Bspline curves and surfaces approximation is performed,
- It is possible to enter a user value for Deformation,
- This option may change the internal structure of BSplines (equations and knots),
- This option usually results in a significant decrease in the number of faces cuttings.
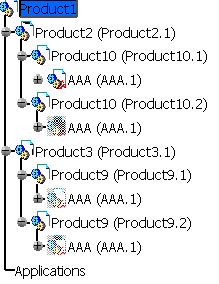
Assemblies physical structure
![]()
This option enables the processing of sub-assemblies of an imported
assembly.
By default, it is not selected. A CATProduct file containing the whole
assembly structure and a CATPart file for each part of the assembly are
created.
If you select this option, a CATProduct file containing the sub-assembly
structure is created for each node of the whole assembly while a CATPart
file is created for each part of the whole assembly.