[ Previous | Next | Table of Contents | Index | Library Home |
Legal |
Search ]
Communications Programming Concepts
Socket header files contain data
definitions, structures, constants, macros, and options used by socket
subroutines. An application program must include the appropriate header
file to make use of structures or other information a particular socket
subroutine requires. Commonly used socket header files are:
| /usr/include/netinet/in.h
| Defines Internet constants and structures.
|
| /usr/include/arpa/nameser.h
| Contains Internet name server information.
|
| /usr/include/netdb.h
| Contains data definitions for socket subroutines.
|
| /usr/include/resolv.h
| Contains resolver global definitions and variables.
|
| /usr/include/sys/socket.h
| Contains data definitions and socket structures.
|
| /usr/include/sys/socketvar.h
| Defines the kernel structure per socket and contains buffer
queues.
|
| /usr/include/sys/types.h
| Contains data type definitions.
|
| /usr/include/sys/un.h
| Defines structures for the UNIX interprocess communication domain.
|
| /usr/include/sys/ndd_var.h
| Defines structures for the operating system Network Device Driver (NDD)
domain.
|
| /usr/include/sys/atmsock.h
| Contains constants and structures for the Asynchronous Transfer Mode
(ATM) protocol in the operating system NDD domain.
|
In addition to commonly used
socket header files, Internet address translation
subroutines require the inclusion of the inet.h file.
The inet.h file is located in the
/usr/include/arpa directory.
The socket data structure defines
the socket. During a socket subroutine, the system dynamically creates
the socket data structure. The socket address is specified by a data
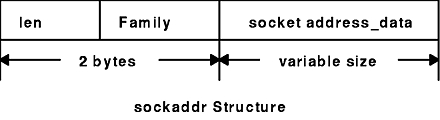
structure that is defined in a header file. See the sockaddr Structure figure for an illustration of this data
structure.
Figure 9-3. sockaddr Structure. This diagram shows the sockaddr structure containing the following from the left: len, family, and socket address_data. The second line of the diagram gives the size of the sections in the first line as follows: len and family together equal 2 bytes, socket address_data is a variable size.
The
/usr/include/sys/socket.h
file contains the sockaddr structure. The contents of the
sa_data structure depend on the protocol in use.
The types of socket-address data
structures are as follows:
| struct sockaddr_in
| Defines sockets used for machine-to-machine communication across a
network and interprocess communication (IPC). The
/usr/include/netinet/in.h file contains the
sockaddr_in structure.
|
| struct sockaddr_un
| Defines UNIX domain sockets used for local IPC only. These sockets
require complete path name specification and do not traverse networks.
The /usr/include/sys/un.h file contains the
sockaddr_un structure.
|
| struct sockaddr_ns
| Defines the Xerox Network Services (XNS) sockets to be used for reliable,
full-duplex, connection-oriented services to an application. The
/usr/include/netns/ns.h file contains the
sockaddr_ns structure.
|
| struct sockaddr_ndd
| Defines the operating system NDD sockets used for machine-to-machine
communication across a physical network. The
/usr/include/sys/ndd_var.h file contains the
sockaddr_ndd structure. Depending upon socket types and
protocol, other header files may need to be included.
|
[ Previous | Next | Table of Contents | Index |
Library Home |
Legal |
Search ]

