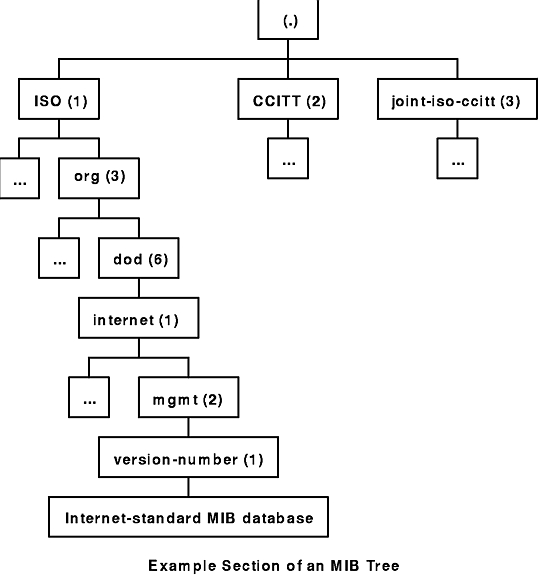
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a database containing the information pertinent to network management. The database is conceptually organized as a tree. The upper structure of this tree is defined in Requests for Comments (RFC) 1155 and RFC 1213. The internal nodes of the tree represent subdivision by organization or function. MIB variable values are stored in the leaves of this tree. Thus, every distinct variable value corresponds to a unique path from the root of the tree. The children of a node are numbered sequentially from left to right, starting at 1, so that every node in the tree has a unique name, which consists of the sequence of node numbers that comprise the path from the root of the tree to the node. The Example Section of an MIB Tree figure illustrates the relationship of sections of the MIB tree.
Figure 7-1. Example Section of an MIB Tree. This diagram shows three roots coming off the MIB tree. Their nodes are labeled (from the left) as follows: ISO (1), CCITT (2), joint-iso-ccitt (3). A child of ISO is labeled org (3), whose child is labeled dod (6). Below dod (6) is internet (1) whose child is mgmt (2). Below mgmt (6) is version-number (1), internet-standard MIB tree is the last child.

Here, the network management data for the Internet is stored in the subtree reached by the path 1.3.6.1.2.1. This notation is the conventional way of writing the numeric path name, separating node numbers by periods. All variables defined in RFC 1213 have numeric names that begin with this prefix.
Note: Future versions of the Internet-standard MIB may have higher version numbers with variable names distinct from earlier versions.
A typical variable value is stored as a leaf, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 7-2. Leaves on an MIB Tree. This diagram shows one branch off the path that is labeled system (1). The variable names that branch off from system (1) are from the left: sysDescr (1), sysObjectid (2), sysUpTime (3), and sysServices (7). These variable names are defined by RFC1155 and RFC1213. The instance values which are below the variable names listed previously are value (0) in all four cases. The instance values are defined by the administrator of the host, in conformance with RFC1157.
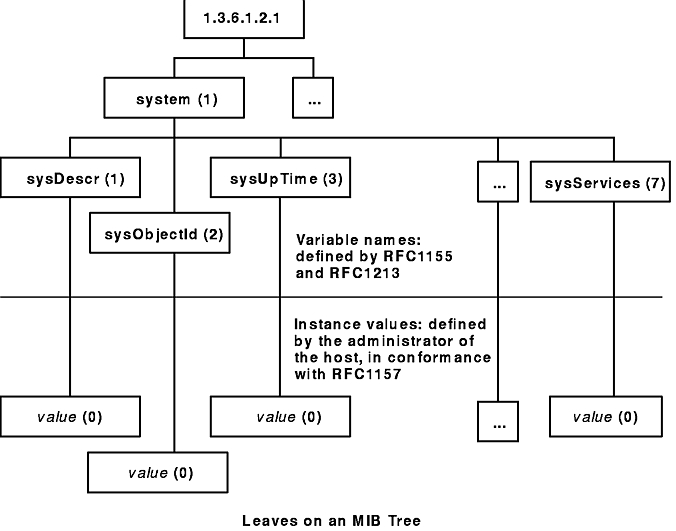
The MIB manager data associates the values of the variables with each uniquely named instance of a variable. For example, 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 is the unique name of the system description, a text string describing the host's operational environment. Because only one such string exists, the instance of the variable name 1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1 (which is denoted by a 0) is reserved for this use only. Many other variables have multiple instances, as illustrated in the Multiple Instance Variables figure.
Figure 7-3. Multiple Instance Variables. This diagram shows ipRouteEntry (1.3.5.1.2.1.4.21.1) at the top of the tree and a branch with the variable name ipRouteAge (10). Both of these variables are defined by RFC1155 and RFC1213. The following instance values branch-off of ipRouteAge (10): value (127.50.50.50) and value (255.25.50.75). Instance values are defined by the administrator of the host, in conformance with RFC1157.
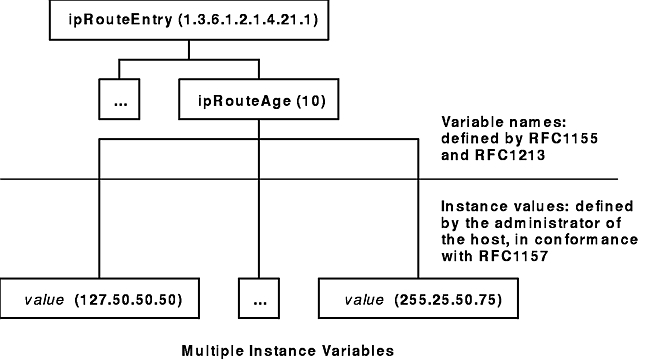
Each variable containing information about a route has an instance that is the Internet Protocol (IP) address of the route's destination. Other variables have more complex rules for forming instances. The variable name uniquely identifies a group of related data, while the variable instance is a unique name for a particular item within the group. For example, 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.10 is the name of the variable whose instances are route ages, while 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.21.1.10.127.50.50.50 is the name of the instance that contains the age of the route to a host with the IP address of 127.50.50.50.
For more information on Internet addresses and routing see "Internet (IP) Addresses" and "TCP/IP Routing"in AIX 5L Version 5.1 System Management Guide: Communications and Networks.