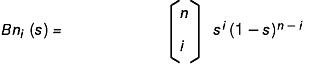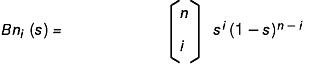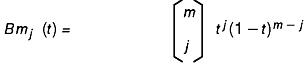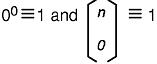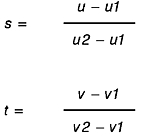[ Previous |
Next |
Contents |
Glossary |
Home |
Search ]
OpenGL 1.1 for AIX: Reference Manual
glMap2 Subroutine
Purpose
Defines a 2-dimensional (2D) evaluator.
Library
OpenGL C bindings library: libGL.a
C Syntax
void glMap2d(GLenum Target,
GLdouble u1,
GLdouble u2,
GLint uStride,
GLint uOrder,
GLdouble v1,
GLdouble v2,
GLint vStride,
GLint vOrder,
const GLdouble *Points)
void glMap2f(GLenum Target,
GLfloat u1,
GLfloat u2,
GLint uStride,
GLint uOrder,
GLfloat v1,
GLfloat v2,
GLint vStride,
GLint vOrder,
const GLfloat *Points)
Parameters
| Target |
Specifies the kind of values that are generated by the evaluator. The following symbolic constants are accepted: |
| GL_MAP2_VERTEX_3 |
|
| GL_MAP2_VERTEX_4 |
|
| GL_MAP2_INDEX |
|
| GL_MAP2_COLOR_4 |
|
| GL_MAP2_NORMAL |
|
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_1 |
|
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_2 |
|
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_3 |
|
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_4 |
|
| u1, u2 |
Specify a linear mapping of u, as presented to glEvalCoord2, to u1, one of the two variables that is evaluated by the equations specified by this subroutine. |
| uStride |
Specifies the number of floats or doubles between the beginning of control point Rij and the beginning of control point R(i+1)j, where i and j are the u and y control-point indexes, respectively. This allows control points to be embedded in arbitrary data structures. The only constraint is that the values for a particular control point must occupy contiguous memory locations. |
| uOrder |
Specifies the dimension of the control point array in the u axis. Must be positive. |
| v1, v2 |
Specify a linear mapping of v, as presented to glEvalCoord2, to v1, one of the two variables that is evaluated by the equations specified by this subroutine. |
| vStride |
Specifies the number of floats or doubles between the beginning of control point Rij and the beginning of control point Ri(j+1), where i and j are the u and v control point indexes, respectively. This allows control points to be embedded in arbitrary data structures. The only constraint is that the values for a particular control point must occupy contiguous memory locations. |
| vOrder |
Specifies the dimension of the control point array in the v axis. Must be positive. |
| Points |
Specifies a pointer to the array of control points. |
Description
Evaluators provide a way to use polynomial or rational polynomial mapping to produce vertices, normals, texture coordinates, and colors. The values produced by an evaluator are sent on to further stages of GL processing just as if they had been presented using the glVertex, glNormal, glTexCoord, and glColor subroutines, except that the generated values do not update the current normal, texture coordinates, or color.
All polynomial or rational polynomial splines of any degree (up to the maximum degree supported by the GL implementation) can be described using evaluators. These include almost all surfaces used in computer graphics, such as B-spline surfaces, non-uniform rational B-spline surfaces (NURBS), and Bezier surfaces.
Evaluators define surfaces based on bivariate Bernstein polynomials. Define p(s, t) as follows:
Let p(s, t) = Bn0Bm0R00 + Bn1Bm0R01 + . . . + BnnBm0Rn0
+Bn0Bm1R01 + . . . + BnnBm1Rn1
.
.
.
+Bn0BmmR0m + . . . + BnnBmmRnm
where Rij is a control point, Bni (s) is the ith Bernstein polynomial of degree:
n (uOrder = n +1)
See the following figure:
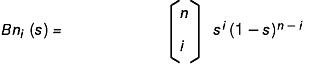
and Bmj (t) is the jth Bernstein polynomial of degree:
m (vOrder = m + 1)
See the following figure:
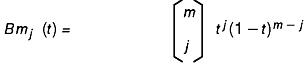
See the following figure:
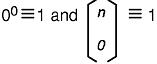
The glMap2 subroutine is used to define the
basis and to specify what kind of values are produced. Once defined, a map can be
enabled and disabled by calling the glEnable and glDisable subroutines
with the map name, which is one of the nine predefined values for the Target
parameter. When the glEvalCoord2 subroutine presents values u and
v, the bivariate Bernstein polynomials are evaluated using s and
t, as in the following figure:
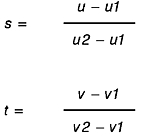
The Target parameter specifies a symbolic constant that indicates what kind of control points are provided in the Points parameter, and what output is generated when the map is evaluated. It can assume one of the following nine predefined values:
| GL_MAP2_VERTEX_3 |
Each control point is three floating-point values representing x, y, and z. Internal glVertex3 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. |
| GL_MAP2_VERTEX_4 |
Each control point is four floating-point values representing x, y, z, and w. Internal glVertex4 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. |
| GL_MAP2_INDEX |
Each control point is a single floating-point value representing a color index. Internal glIndex subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current index is not updated with the value of these glIndex subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_COLOR_4 |
Each control point is four floating-point values representing red, green, blue, and alpha. Internal glColor4 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current color is not updated with the value of these glColor4 subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_NORMAL |
Each control point is three floating-point values representing the x, y, and z components of a normal vector. Internal glNormal subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current normal is not updated with the value of these glNormal subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_1 |
Each control point is a single floating-point value representing the s texture coordinate. Internal glTexCoord1 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current texture coordinates are not updated with the value of these glTexCoord subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_2 |
Each control point is two floating-point values representing the s and t texture coordinates. Internal glTexCoord2 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current texture coordinates are not updated with the value of these glTexCoord subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_3 |
Each control point is three floating-point values representing the s, t, and r texture coordinates. Internal glTexCoord3 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current texture coordinates are not updated with the value of these glTexCoord subroutines. |
| GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_4 |
Each control point is four floating-point values representing the s, t, r, and q texture coordinates. Internal glTexCoord4 subroutines are generated when the map is evaluated. However, the current texture coordinates are not updated with the value of these glTexCoord subroutines. |
The uStride, uOrder, vStride, vOrder, and Points parameters define the array addressing for accessing the control points. The Points parameter is the location of the first control point, which occupies one, two, three, or four contiguous memory locations, depending on which map is being defined. There are uOrder times vOrder control points in the array. The uStride parameter tells how many float or double locations are skipped to advance the internal memory pointer from control point Rij to control point R(i+1)j. The vStride parameter tells how many float or double locations are skipped to advance the internal memory pointer from control point Rij to control point Ri(j+1).
Notes
For all GL subroutines that accept pointers to data, it is as if the contents of Points were copied by glMap2 before it returned. Changes to the contents of Points have no effect after glMap2 is called.
Errors
| GL_INVALID_ENUM |
Target is not an accepted value. |
| GL_INVALID_VALUE |
u1 is equal to u2, or if v1 is equal to v2. |
| GL_INVALID_VALUE |
uStride or vStride is less than the number of values in a control point. |
| GL_INVALID_VALUE |
uOrder or vOrder is less than one or greater than GL_MAX_EVAL_ORDER. |
| GL_INVALID_OPERATION |
The glMap2 subroutine is called between a call to glBegin and the corresponding call to glEnd. |
Associated Gets
Associated gets for the glMap2 subroutine are as follows. (See the glGet subroutine for more information.)
glGetMap
glGet with argument GL_MAX_EVAL_ORDER
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_VERTEX_3
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_VERTEX_4
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_INDEX
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_COLOR_4
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_NORMAL
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_1
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_2
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_3
glIsEnabled with argument GL_MAP2_TEXTURE_COORD_4.
Files
| /usr/include/GL/gl.h |
Contains C language constants, variable type definitions, and ANSI function prototypes for OpenGL. |
Related Information
The glBegin or glEnd subroutine, glColor subroutine, glEnable or Disable subroutine,
glEvalCoord subroutine, glEvalMesh subroutine, glEvalPoint subroutine, glGetMap subroutine, glIndex subroutine, glMap1 subroutine,
glMapGrid subroutine, glNormal subroutine, glTexCoord subroutine, glVertex subroutine.
OpenGL Overview.
[ Previous |
Next |
Contents |
Glossary |
Home |
Search ]