Feel free - send a
 for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
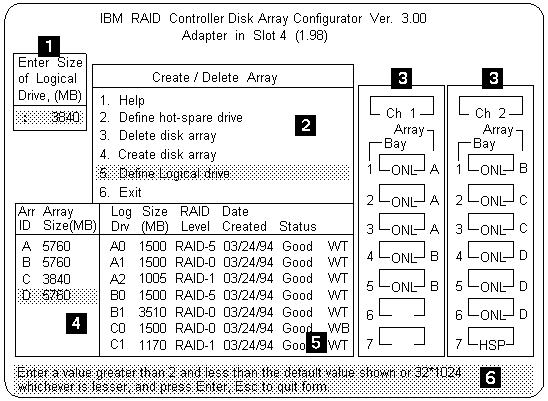
When you need to confirm an action, the Confirm pop-up appears in this area.
NOTE:
The Channel/Bay/Array area on the screen does not reflect the physical
configuration of the server. The hot-swappable hard disk drives are numbered 1
through 6 (from left to right from top to bottom).
See 'Installing Internal Drives' to see the physical location of the hard disk drives.
NOTE: The capacity (size) is shown in binary equivalent.
When a drive is being rebuilt, this area, along with the Logical Drive list area, shows the progression of the rebuilding process.
The status of the logical drive is also shown.
Good means that all is well with the drive.
Critical means that you must replace the drive or do a rebuild
operation. (You will have received a message telling you the drive is in a
Critical state.)
Offline means that the logical drive is unrecoverable, the data
in that drive is lost.
When a drive is being rebuilt, this area, along with the Array list area, shows the progression of the rebuilding process.
NOTE: The capacity (size) is shown in binary equivalent.
During an initialization process, the Write Policy area displays the percent initialized, during a synchronization process, it displays the percent synchronized.
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.