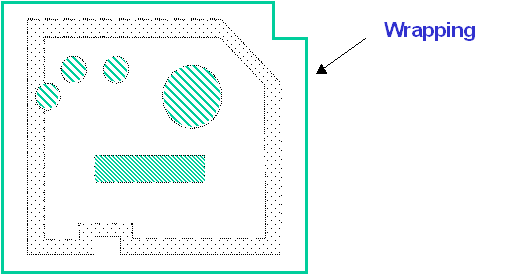
The following section aims at describing wrapping operation in more
details:
How is the Wrapping Representation Calculated?
You generate a wrapping from existing geometric elements by:
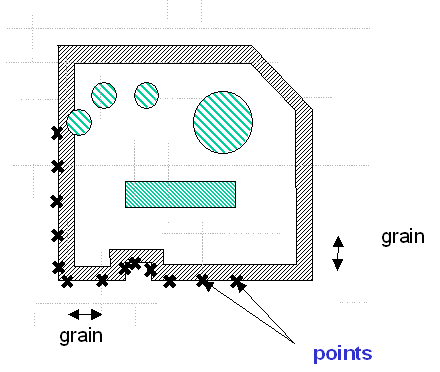
- computing a set of points regularly spaced on the envelope of the
original geometry (distance between points = grain parameter)
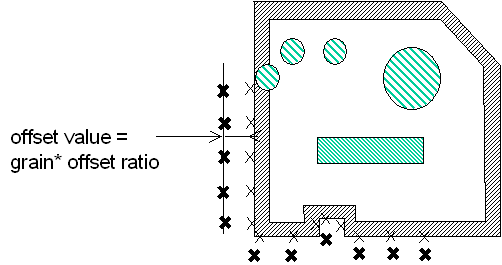
- offsetting these points to obtain a inflated result which better
includes the original geometry (offset value = grain * offset ratio)
- building triangles from the set of offset points.
The following example aims at illustrating these three steps as well as
the impact of grain and offset ratio parameters on the final result.
Step 1: Computing Points Using the Grain
Parameter
Step 2: Offsetting Points Using the
Offset Ratio Parameter
Step 3: Building the Result 
Case 1: Offset Ratio = 0.0
|
Case 2: Offset Ratio = 0.5
|
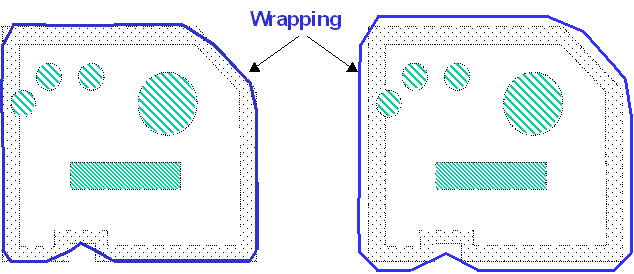 |
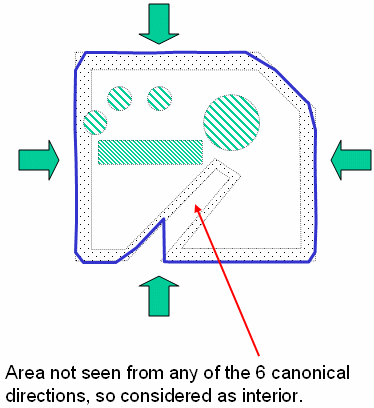
Particular Case: illustration of how the frontier between inner area
and outer area is calculated:
Case 3: Cubic option set
When the cubic check box is selected, the result is a voxel (cubic)
representation of the envelope. The voxel size equals the grain parameter.
The offset ratio is not used.
How the Grain and Offset Parameters Impact the
Wrapping Calculation?
The table below shows the grain parameter impact on the wrapping
calculation:
Grain Value
|
Computation Time
|
Used Memory
|
Resulting Size (number of triangles)
|
 Greater Greater |
 Shorter Shorter |
 Less Less |
 Smaller Smaller |
 Smaller Smaller |
 Longer Longer |
 More More |
 Bigger Bigger |
The table below shows the offset ratio impact on the wrapping
calculation:
Offset Ratio Value
|
Computation Time
|
Used Memory
|
Resulting Geometric Size
|
Resulting Size
(number of triangles)
|
 Greater Greater |
No Change |
No Change |
Bigger |
No change |
 Smaller Smaller |
No Change |
No Change |
Smaller |
No Change |
| Cubic Mode |
 Shorter Shorter |
 Less Less |
Includes entirely the
original geometry |
No Change |
|