This overview provides the following
information:
Flex Physical Simulation in a Nutshell
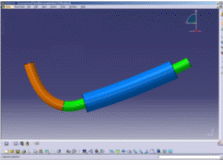
Simulating the behavior of cables (FLEX) using integrated CAD-CAE tools during the product design process is an important requirement in the automotive and aerospace industries. Real components such as flexible tubes, hoses, wires and electrical wires are so flexible that their shape depends totally on the context in which they are used. This behavior has to be correctly taken into account in design and simulation processes.
Flex Physical Simulation is a product dedicated to simulate flexible
slender bodies taking into account their physical properties.
This product provides other applications, such as Electrical Harness Installation, the functionalities needed to model flexible slender bodies (flex) from the flex definition to its complete flexible behavior in simulation.
Flex Definition

A flex is represented by a:
- 3D curve/line called the neutral fiber
- variable cross-section
A typical example of a variable cross-section is as shown: 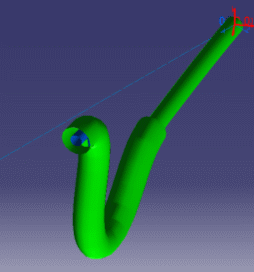
Cross-Sections
|
|
Only orthotropic
cross-sections are supported An orthotropic
cross-section has two symmetry planes meaning the shear section has to
fit with the centroid of the section. |
|
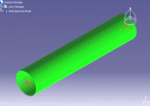 circular cross-section |
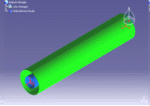 annular cross-section |
|
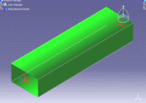 rectangular cross-section |
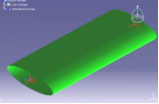 arbitrary orthotropic cross-section (elliptic) |
|
Material properties
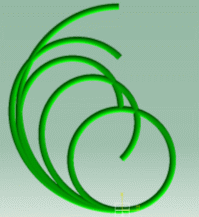
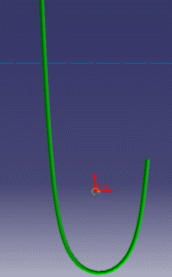
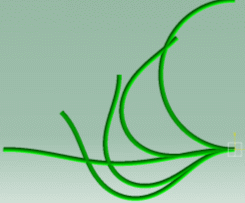
Flex Physical Simulation product exhibits particular local deformation modes (behavior) of the flex:
-
traction-compression (in axial direction)
-
torsion (around axial direction)
-
bending-shearing (in orthogonal planes containing axial direction)
These are examples of more or less flexible flex subjected to gravity with ends imposed to displacements.
 |
|
 |
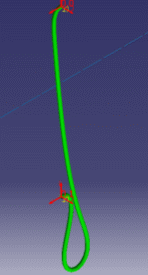 |
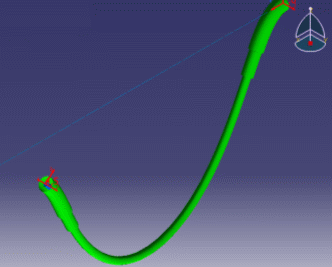 |
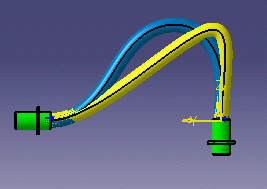
FLEX Added Values
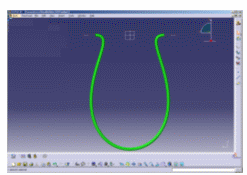
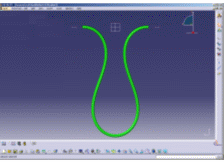
The illustrations below aim at showing you the added value of FLEX in terms of realistic shapes.
Standard algorithm vs FLEX algorithm |
|
 |
|
|
|
Legend:
|
EHI |
EHI With FLEX |
| The covering adds a rigidity that is taken into account by Flex | |
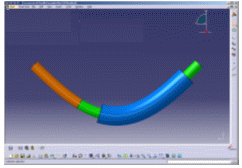 |
 |
| Example of the gap that can appear on the curvature. | |
 |
 |
![]()