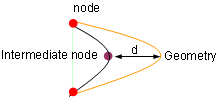
This task shows you how to create a 2D mesh using triangle elements.
This command is available both in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench and in the Advanced Meshing Tools workbench. Options available in the Octree triangle mesher are different depending on the products you have installed:
Generative Part Structural Analysis (GPS) or FEM Solid (FMD)
In this configuration, the dialog box allowing you to define Octree 2D mesh parts contains only two tabs either in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench or in the Advanced Meshing Tools workbench.
-
Click Octree Triangle Mesher
 (in the Model Manager toolbar for the Generative Structural
Analysis workbench or the Meshing Methods toolbar for the
Advanced Meshing Tools workbench).
(in the Model Manager toolbar for the Generative Structural
Analysis workbench or the Meshing Methods toolbar for the
Advanced Meshing Tools workbench). -
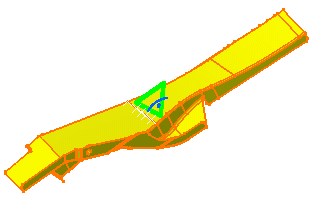
Select the 2D geometry.
A symbol appears on the geometry and the OCTREE Triangle Mesh dialog box appears.

-
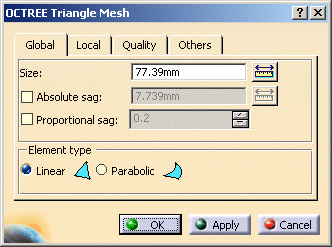
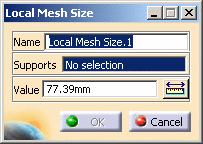
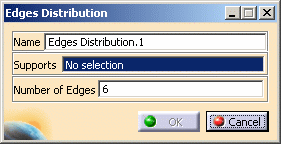
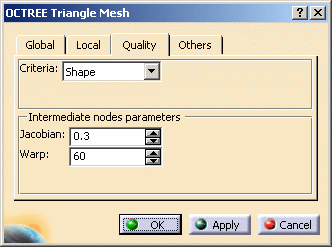
Global tab: lets you change global parameters.
To know more, refer to the global tab description. -
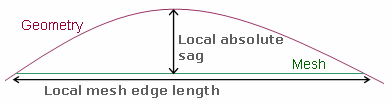
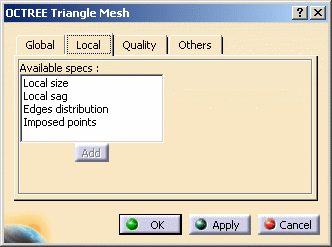
Local tab: lets you create local parameters.
To know more, refer to the local tab description.
-
-
Modify the desired options. In this particular case, keep the default options.
-
Click OK.
The OCTREE Triangle Mesh.2 mesh parts appears in the specification tree. Note that now the corresponding 2D Property is missing. For more details on how to add this property, refer to Generative Structural Analysis User's Guide - User Tasks - Model Manager - Creating 2D Property.


You can change the physical property of the 2D mesh element you have just created using the Changing Type contextual menu.
-
2D mesh can be deleted and/or added to parts manually.
-
To visualize the mesh in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench, use the Mesh Visualization contextual menu.
The mesh is automatically displayed in the Advanced Meshing Tools workbench.