This task shows the various methods for creating planes:
Open the Planes1.CATPart document.
For instance, if you choose the Through two lines type, you are not able to select a plane. May you want to select a plane, choose another type in the combo list.
Offset from plane
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Offset from plane plane type.
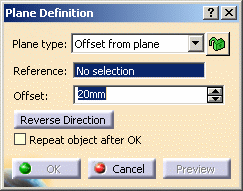

Once you have defined the plane, it is represented by a green square symbol, which you can move using the graphic manipulator. -
Select a reference Plane then enter an Offset value.
A plane is displayed offset from the reference plane. 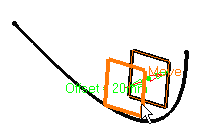
-
Click Reverse Direction to reverse the change the offset direction, or simply click on the arrow in the geometry.
-
Click Repeat object after OK if you wish to create more offset planes.
In this case, the Object Repetition dialog box is displayed, and you key in the number of instances to be created before pressing OK. 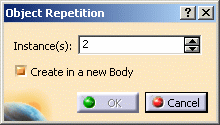
As many planes as indicated in the dialog box are created (including the one you were currently creating), each separated from the initial plane by a multiple of the Offset value. 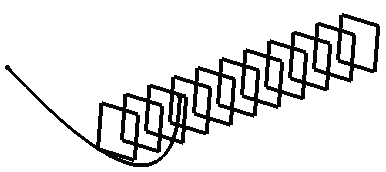
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Parallel through point
-
Click Plane
 .
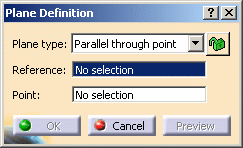
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Parallel though point plane type.
-
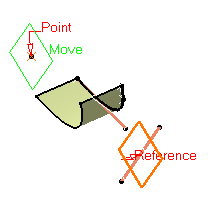
Select a reference Plane and a Point. A plane is displayed parallel to the reference plane and passing through the selected point.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Angle/Normal to plane
-
Click Plane
 .
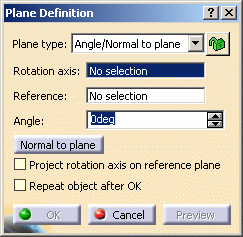
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Angle/Normal to plane plane type.
-
Select a reference Plane and a Rotation axis.
This axis can be any line or an implicit element, such as a cylinder axis for example. To select the latter press and hold the Shift key while moving the pointer over the element, then click it. -
Enter an Angle value.
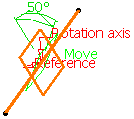
The plane is displayed such as its center corresponds to the projection of the center of the reference plane on the rotation axis. It is oriented at the specified angle to the reference plane. -
Check Project rotation axis on reference plane if you wish to project the rotation axis onto the reference plane. If the reference plane is not parallel to the rotation axis, the created plane is rotated around the axis to have the appropriate angle with regard to reference plane.
-
Check Repeat object after OK if you wish to create more planes at an angle from the initial plane.
In this case, the Object Repetition dialog box is displayed, and you key in the number of instances to be created before pressing OK. 
As many planes as indicated in the dialog box are created (including the one you were currently creating), each separated from the initial plane by a multiple of the Angle value. Here we created five planes at an angle of 20 degrees. 
This plane type enables to edit the plane's parameters. Refer to Editing Parameters to find out how to display these parameters in the 3D geometry. -
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Through three points
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Through three points plane type.
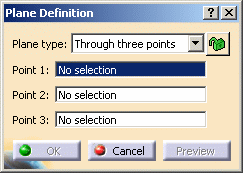
-
Select three points. A plane passing through the three points is displayed. You can move it simply by dragging it to the desired location.
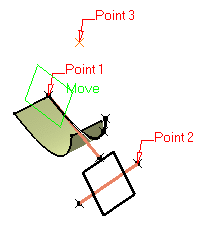
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Through two lines
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Through two lines plane type.
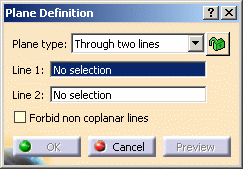
-
Select two lines.
The plane passing through the two line directions is displayed.
When these two lines are not coplanar, the vector of the second line is moved to the first line location to define the plane's second direction.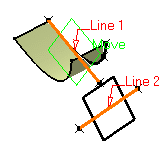
-
Check Forbid non coplanar lines to specify that both lines be in the same plane.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Through point and line
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Through point and line plane type.
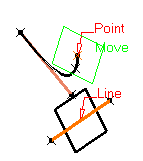
-
Select a Point and a Line. A plane passing through the point and the line is displayed.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Through planar curve
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Through planar curve plane type.

-
Select a planar Curve. A plane containing the curve is displayed.
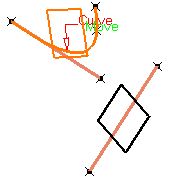
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
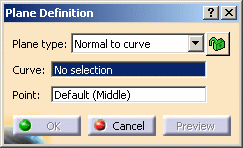
Normal to curve
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Normal to curve plane type.
-
Select a reference Curve.
-
You can select a Point. By default, the curve's middle point is selected.

It can be selected outside the curve. A plane is displayed normal to the curve with its origin at the specified point. The normal is computed at the point on the curve that is the nearest to the selected point. 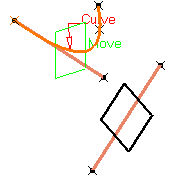
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
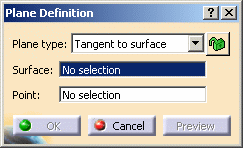
Tangent to surface
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Tangent to surface plane type.
-
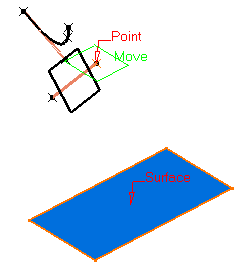
Select a reference Surface and a Point. A plane is displayed tangent to the surface at the specified point.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Equation
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Equation plane type.
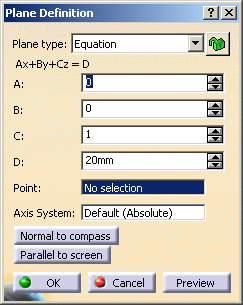
-
Enter the A, B, C, D components of the Ax + By + Cz = D plane equation.
-
Select a point to position the plane through this point, you are able to modify A, B, and C components, the D component becomes grayed.
When the command is launched at creation, the initial value in the Axis System field is the current local axis system. If no local axis system is current, the field is set to Default.
Whenever you select a local axis system, A, B, C, and D values are changed with respect to the selected axis system so that the location of the plane is not changed. This is not the case with values valuated by formulas: if you select an axis system, the defined formula remains unchanged. -
Click Normal to compass to position the plane perpendicular to the compass direction.
-
Click Parallel to screen to position the plane parallel to the screen current view.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Mean through points
-
Click Plane
 .
.The Plane Definition dialog box appears. -
Select the Mean through points plane type.
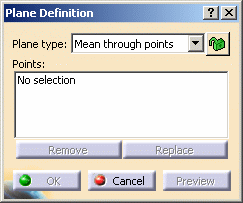
-
Select three or more points to display the mean plane through these points.
It is possible to edit the plane by first selecting a point in the dialog box list then choosing an option to either: - Remove the selected point
- Replace the selected point by another point.
-
Click OK to create the plane.
The plane (identified as Plane.xxx) is added to the specification tree.
Parameters can be edited in the 3D geometry. For more information, refer to the Editing Parameters.
You can isolate a plane in order to cut the links it has with the geometry used to create it. To do so, use the Isolate contextual menu. For more information, refer to the Isolating Geometric Elements.
![]()