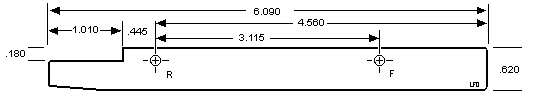|
Lacuna vs. Bermuda
Bermuda Planar
9577 Power Supply: 197W Lacuna vs. Bermuda
The easiest method to differ a Lacuna planar from any other is looking
at it from the rear (connector side). If there is a 15-pin triple-row video
connector in line with keyboard, mouse, serial and parallel - it is a "Lacuna"
planar. Bermuda Models have a 60-pin IBM RS/6000 style SCSI connector there.
9576 and 9577 Model Codes Dxx=Choice of OS Kxx=OS/2 2.1 Qxx=DOS/Windowze 3.1 1xx=MM (Ultimedia) xNx=DX2-66 (5v) xUx=SX-33 (5v) xxA=212MB SCSI xx6=104MB SCSI xxF=400MB SCSI 9577 Ultimedia
Model Features
9576 and 9577 i/s Model Codes Thanks for showing the EASY way, Oloruin! Axx=Lacuna, On-board IDE, built-in S3 video
9577S Multimedia Model Features All the multimedia models include the following features:
Ed. I found NO
MM 76 models.
Upgrading planars You can upgrade any current PS/2 76/77 or PS/2 56/57 with the new PS/2 Planar Upgrade. You'll gain all the advantages of the new 76/77 i and s systems. Current 76/77 systems will perform up to 38% faster while keeping everything else intact. Devil's in the
Details
The two broad classes of box designs that led to the 9576
and 9577.
Taller box:
Of course, the 855X were 80386DX or 80386SLC, so they used a completely different system board. The 9576 and 9577 used the same system board (=Bermuda), one with SCSI built into the board (=Bermuda). The 9576i and 9577i (Lacuna system board) were made in two different clock speeds -- 25MHz and 33MHz. Their system board FRU part numbers were: 25MHz only: 95G9691 (not streaming transfer
capable)
A 957Xs is only a 957Xi with a modified Future Domain SCSI
card added to one of the adapter slots on the bus riser card, to handle
internal/external SCSI devices.
Parts Comparison:
9576 Bus adapter*
87F4833
9556 Bus adapter*
79F7210
8556 Bus adapter*
79F7210
9577i/s 5-slot bus riser assembly
68G2709
9577 Bus adapter riser
card 87F4836
9557 Bus adapter riser
card 41G3877
8557 Bus adapter riser
type 1 85F0056
So you see, it is important to know both the part number
and clock speed limitation of the Lacuna-type board, and to have the correct
bus riser card for the particular box/system board. In other words, you
cannot really upgrade a 957X to a 957Xi/s without changing the riser card
as well as the system board!
9576i / 9577i Processor Upgrade Jumper settings
for CPU upgrades
IBM 76 Security Cable Cover . Hmm, never seen one. MULTIMEDIA MODELS
The pinout of the standard 9577 speaker/power switch module is 
Not supported o IBM PS/2 8514 Display Adapter/A (#4054, 1887972) o IBM PS/2 Micro Channel SCSI Adapter (#1005, 6451109) o IBM PS/2 Micro Channel SCSI Adapter with Cache (#1018, 6451110) o IBM Mwave WindSurfer-MCA Communication Adapter/A (#7058, 82G7058) The IBM 1GB AT Hard Disk Drive (#2543, 70G8512) is supported with the following limitation: If you experience problems configuring this drive as the "master" with any other fixed disk drive in your system, reconfigure this drive as the "slave" drive. Secured removable media via 2.88MB Electronic Eject Diskette Drive (optional)
77 5.25" Drive Bay Guides 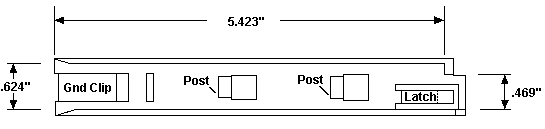
Post- Notches on the reverse that fit into the drive bay walls. Latch- Locks the guide onto the drive bay wall. Guide FRUs
To remove Guides
This was "fun". On this rail, the screw hole marked "R"
was the fixed hole, and it serves as the reference point for the important
surfaces. Note that the center-to-center distance is 3.115". Measured that
from a drive. One hole is usually slotted so there can be some variation
between mounting screw locations on drives.
5.25" 77 Drive Rail
Hack
PCMCIA Adapter mounting I finally got around to installing the PCMCIA adapter in my 77s. The trick- mount the adapter on a 76/77 floppy tray. (Adapter MUST be in the stamped metal bay PN 64F1270) Remove the rail guides on the dive support stucture in the 77. (Catches are on the inner end) swap the guides to the other side and push them onto the mounting studs. Now turn the tray/adapter upside down and push it into the rails. Note that the two card ejection buttons are now on the left side of the adapter. Just happens to be the exact height to perfectly fit the bezel. Fixed Disk Bay 4C Drive Slide 96F7775, 71G5706, 71G5708, 79F3300 9577 Air Baffle
for Fixed Disk Bay 4C FRU 92F0251
The older 8557 and 9557 used a grey colored baffle, same FRU. This was used in older systems with hot running drives in 4C. Modern 1" high drives should run cool enough without it, but if you want to run a 7,200RPM (or higher) drive in your 77, you MIGHT want to help cool it as much as possible. Pasteboard
hack
PS/2 - 76/77 S Model Configures SCSI HD As 6,1 Symptom: The 9576 or 9577 system configures the harddisk with a SCSI ID of 6,1 instead of 6,0. A POST error of 1047000 107 may also occur. Problem Isolation Aids:
Fix:
|