RAID Level-0
RAID Level-0
RAID level-0 stripes the data across all the drives in the array.
This offers substantial speed enhancement, but provides for no data redundancy.
RAID level-0 provides the largest capacity of the RAID levels offered, because no room is taken up
for redundant data or data-parity storage.
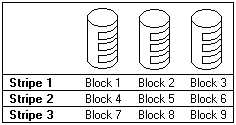
The following illustration shows data arranged in an array of three hard disk drives defined as one RAID level-0 logical drive.
Notice that the data is striped across all the drives in the array, but no copies of the data or parity information is stored.
A hard disk failure within the array results in loss of data in the logical drive assigned RAID level-0,
but only in that logical drive .
If you have logical drives assigned RAID level-1 or level-5 in the same array, they will not lose data.
Note: The ServeRAID controller automatically assigns RAID level-0 to all logical drives
in an array containing only one hard disk drive.
When you replace a failed drive, the ServeRAID controller can rebuild all the RAID level-1 and RAID level-5 logical drives
automatically onto the replacement hard disk drive.
However, any data stored in a failed RAID level-0 logical drive is lost.
Though the risk of data loss is present, you might want to assign RAID level-0 to one of the logical drives to take advantage
of the speed offered with this RAID level. You could use this logical drive to enter data that you back up each day and for which
safety is not of primary importance, that is, data that you can re-create easily.
You also might want to use a RAID level-0 logical drive when the work you are doing requires maximum capacity.
Please see the LEGAL - Trademark notice.
Feel free - send a  for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.


 for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.
for any BUG on this page found - Thank you.