 |
This task shows you how to migrate V4 data into V5 in
a User Defined mode, that is to say how to migrate the entire V4 models
data into V5 formats data (in the V4/V5 batch). The
User Defined mode allows you to choose
some elements belonging to a single V4 model and migrate only them with the
same rules as for complete mode regarding the Structuration option.
With the User Defined mode, you can
use the V4 >V5 batch Structuration capability but only on a part of a V4
model. The
User Defined mode
will take the same options as the Complete mode. A
Structuration (for
instance by solid) is defined because of the options chosen by the end
user are exactly the same as for the Complete mode. A format (as specs or as result)
must also be defined. |
 |
- Open a
CATIAV4 model in CATIA V5.
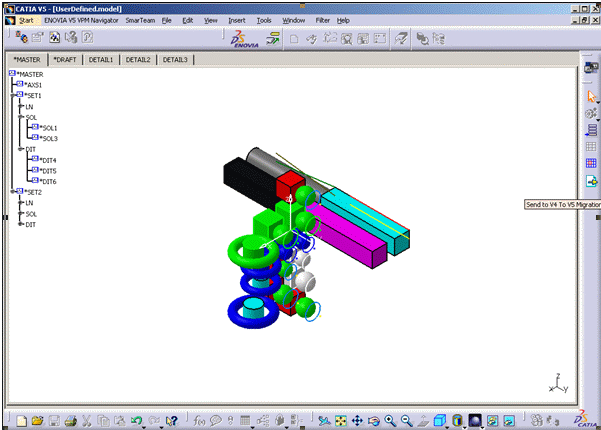
-
Click the geometrical representation and
select
the first element to migrate. For example, in this case: *SOL3.
- Select
Send to V4ToV5Migration
to migrate the first element.
A window with migration
options is displayed.
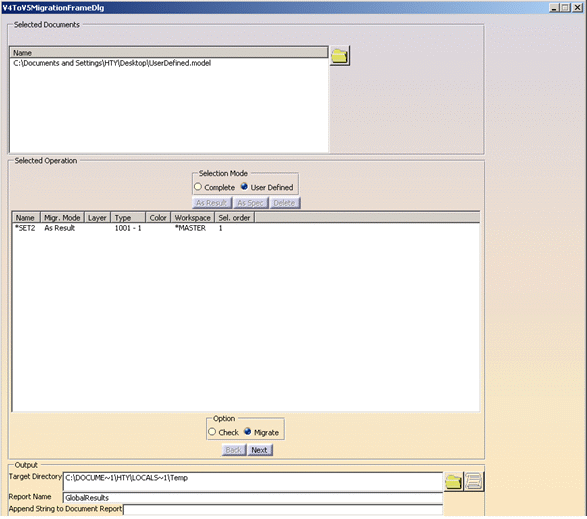
The design of this interface is similar
to the interface used in the CATUTIL process, when launching the
classical batch mode. The model path is automatically set,
the User Defined option is set (note , there is a limitation: no complete mode is available here. If selected, only a
re-usable XML file is created) and some characteristics of
the selected element appear. These characteristics are:
-
the name of the element (using its
V4 identifier)
-
the format chosen for migration
(As Spec or As Result) which can be modified for any
element
-
the layer in which the element is
set
-
the type of the element
-
the color of the element (with its
V4 code value)
-
the workspace of the element
-
a number representing the order of
selection
-
Check/Migrate options and some
fields for output documents are available.
-
You can select and
de-select (by using Delete
button) the elements as often as needed. The rules are the
following:
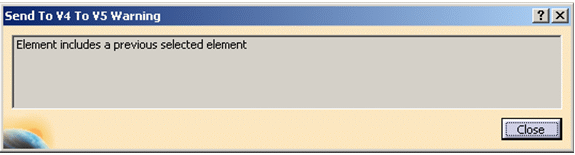
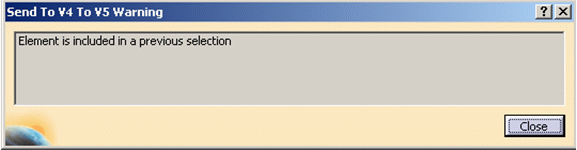
-
if an element is selected and,
after that, an element including it is selected, the
first one is replaced by the second one.
-
If the second one is de-selected,
the first one will be back. For example: if *SOL1
belongs to *SET1 and if both are selected (*SOL1 first),
only *SET1 is taken into account. If it is de-selected,
*SOL1 replaces it. The following message appears:
-
When the selection is
confirmed, you can either Run
the batch to make its conversion or
Save the selection into a
XML file. The selection cannot be modified
after that.
-
With the
Back and
Next
buttons, the user can customize the migration, like in Complete mode
(Structuration elements, SPACE and DRAW, etc). For more information
about these options, please refer to
Migrating from V4 To V5 in Batch Mode.
Selection from the specification tree
-
Select Send to V4ToV5Migration.

-
Select Send
to V4 To V5 Migration:
Selection from the Edit menu
-
Select the
appropriate element the user wants to add as below:
-
Select Send to
V4 To V5 Migration:
Saving Information in a XML file
-
After selecting
the element, save it in an XML file using the
Save button.
This allows to postpone the
migration if needed. The XML file can be loaded whenever
required and the migration can be launched with the same
information.
In User Defined mode, it is
not possible to read an XML File. If you try to read a User
defined XML, a warning is displayed. In the CATUTIL, you can
read XML file:
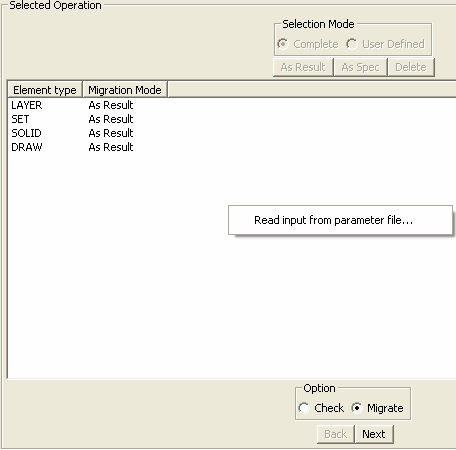
Reading Information from a XML file
(via the Read input from parameter file)
-
Only XML
complete mode case be read. A File
Selection window appears, allowing
to open the XML file.
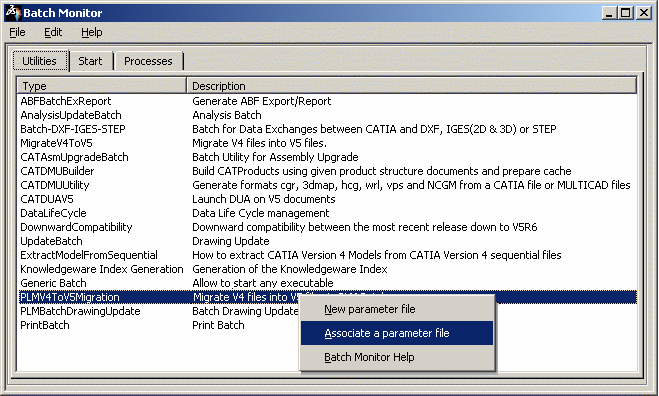
Reading Information from a XML file (via the Associate a parameter
file command)
-
Right-click
PLMV4ToV5Migration
and select Associate a parameter file. With this functionality, you
can open a defined mode XML or a complete mode XML (if an XML file
has been saved). Then, a File Selection window appears, allowing you
to launch the migration.
-
The data conversion can be launched
either from the windows or from CATUTIL using the
Associate parameter file
capability (if a XML file
has been saved).
|
|
|
-
The
User Defined mode is available only with a single model.
If some elements are selected in a Detail, the entire
Detail is migrated. If a Ditto is selected, the
corresponding Detail will be migrated too. The user can
only select one or several elements in the *MASTER
except DETAIL elements or one element in a DETAIL (which
is equivalent to select the DETAIL itself), and except
any other workspace element.
A warning is displayed at the Selection step if an
inappropriate element is selected.
-
About
documents' naming: some documents may seem to be badly
numbered. If a single solid, for instance *SOL3, is
selected in a Solid Structuration option, its name
suffix may be different from xSol3_1. The name chosen
for the document corresponds to the name that would
exist in the Complete mode.
It can happen that a highest level document contains
only one sub-document especially when the chosen
Structuration is by Ditto or by Set / Ditto. In that
case, there is no warning.
-
For
non-exploded Structuration modes (Ditto, Set / Ditto,
Solid / Ditto and Solid / Set / Ditto), if several
Dittos pointing the same Detail (belonging to the
*MASTER) are selected, their chosen formats should be
the same. Indeed, the format of the Ditto is reported on
its pointed Detail and it cannot be different from its
other instances.
The migration is made but the format used for the
pointed Detail may be chosen at random.
-
With
the User Defined mode, the migration of 3D elements can
only be done with the Space option, and the migration of
2D Details can be done with the
Draw
option only.
|
|