This first task will show you how to load a .CATPart document (and display the corresponding specification tree) by entering the Generative Structural Analysis workbench and defining that you will create a Static Analysis case.
Creating a static analysis case means that you will analyze the static boundary conditions of the CATAnalysis document one after the other.
Avoid having CATAnalysis documents automatically saved. Otherwise, on some models, each computation will be followed by a Save operation, thus making temporary data become persistent data.
To know more, refer to Computing Objects Sets.
In this example, a material has been previously assigned to the part you will open. In the case no material has been previously assigned to the part, before entering the Generative Structural Analysis workbench, you should proceed as follows:
-
Select the part in the specification tree.
-
Click Apply Material
 .
.The Material library appears.
-
Select a material family, then select the desired material from the displayed list, then click OK.
The material is applied.
You can visualize the material properties and its analysis characteristics by selecting the material in the specification tree and using Edit > Properties > Analysis.
If you select Start > Analysis & Simulation > Generative Structural Analysis from a CATPart document containing a part without any material assigned, the material library will appear directly for an easy material selection.
-
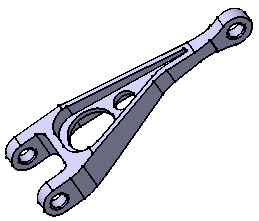
Open the CATPart Document.
To do this, select File > Open, then select the desired .CATPart file.
In this tutorial, you will open CATPart named sample01.CATPart.This opens a Part Design document containing the selected part.
-
Define the View Mode.
To do this, select View > Render Style > Customize View.
The Custom View Modes dialog appears: select the Shading option and then the Material option in the Custom View Modes dialog box.
-
Enter Generative Structural Analysis Workbench.
Select Start > Analysis & Simulation > Generative Structural Analysis.

The New Analysis Case dialog box appears with Static Analysis as default option.
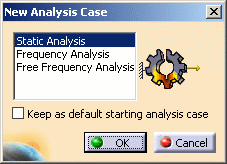
- Static Analysis means that you require a linear static computation by referencing restraints and loads.
- Frequency Analysis means that you require a computation of eigen frequencies by referencing restraints and masses.
- Free Frequency Analysis means that you require a computation of eigen frequencies by referencing only masses (no restraint).
- Keep as default starting analysis case means that when you next select the Start > Analysis and Simulation> Generative Structural Analysis menu, the selected case appears as default.
-
Select an Analysis Case type in the New Analysis Case dialog box.
In this particular case, also keep Static Analysis type selected.
-
Click OK.
The CATAnalysis document now opens. It is named Analysis1. You will now perform different operations in this document.
A link exist between the CATPart and the CATAnalysis document.
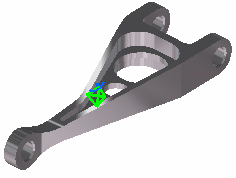
Double-clicking on the green symbol allows displaying mesh specifications or setting meshing parameters.
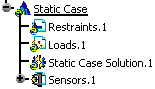
The standard structure of the Analysis specification tree is displayed.
As you can see below, the Finite Element Model contains a Static Case, which contains empty Restraints and Loads objects sets, along with an empty Static Case Solution.1 object set. All along this tutorial, you will assign a Restraint and a Load to the CATAnalysis document and then compute the Static Case Solution.
![]()