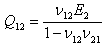The purpose of this test is to check laminated plates with
orthotropic materials.
You will use 2D meshes.
Reference:
Mechanics of Composite Materials, Robert M. Jones, Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, chap 5.5.1, p270.
 Specifications
Specifications
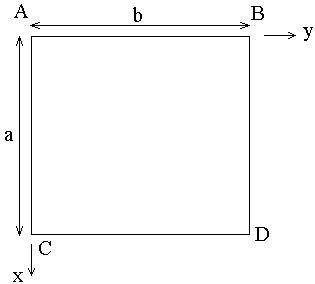
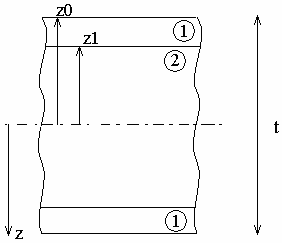
Geometry Specifications
|
a = 0.1 m |
|
|
|
|
Analysis Specifications
|
 |
|
|
|
Mesh Specifications:
|
|
|
Restraints (User-defined): |
 Results
Results
Analytical Results
|
|
|
For a simply supported plate, we have:
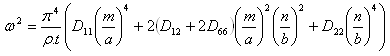
where:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conditions for a specially orthotropic material are:
-
D11 / D22 = 10
-
D12 + 2D66 = 1
m: transversal vibration mode
n: longitudinal vibration mode
Computed Results
|
Modes |
Reference results [Hz] |
Computed results [Hz] |
Normalized results |
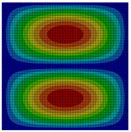
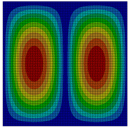
Visualization |
|
m = 1 |
242.724 |
242.16 |
0.997676 |
|
|
m = 1 |
390.785 |
389.992 |
0.997971 |
|
|
m = 1 |
702.403 |
701.991 |
0.999413 |
|
|
m = 2 |
880.240 |
874.553 |
0.99354 |
|
To Perform the Test:
The orthotropic_laminates.CATAnalysis document presents a complete analysis of this case.
To compute the case, proceed as follow:
-
Open the CATAnalysis document.
-
Compute the case in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench.