This test lets you check analysis results for the thermal expansion of a beam, in the context of a static case. You will use 3D mesh with tetrahedron and hexahedron elements.
Reference:
Thermal Expansion Theory
 Specifications
Specifications
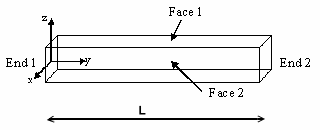
Geometry Specifications
|
Length: |
|
|
Section (square): |
Analysis Specifications
|
Young Modulus (material): |
|
|
Poisson's Ratio (material): |
|
|
Thermal Expansion Coefficient: |
|
|
Mesh Specifications: |
|
|
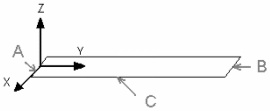
Restraints:
|
|
|
Loads:
The environment temperature is T0 = 300 K |
 Results
Results
- The analytic solution is:
|
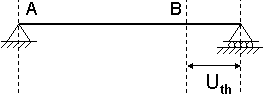
Case 1: |
 |
|
|
Case 2: |
 |
|
|
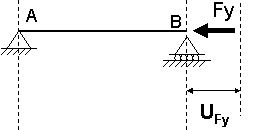
Case 3: |
 |
- The computed results correspond to:
- Uth: Maximal elongation at End 2 under thermal expansion effect.
- σ22: Mean stress tensor of the beam, when the two extremities are clamped.
- Uth- UFy: Maximal final displacement at End 2, when the force Fy is opposed to the thermal expansion.
The computed results are the same for the following elements: TE4, TE10, HE8, HE20, TR3, TR6, QD4, QD8, bar (linear and parabolic):
|
Case |
Quantity |
Analytical solution |
Computed results |
|
Case 1 |
Uth[mm] |
0.2925 |
0.2925 |
|
Case 2 |
σ22 [MPa] |
-58.5 |
-58.5 |
|
Case 3 |
Uth- UFy [mm] |
0 |
0 |
To Perform the Test:
The Thermal_expansion_of_a_beamTE10.CATAnalysis document presents the complete analysis of this case, computed with a parabolic tetrahedron elements (TE10).
The Thermal_expansion_of_a_beamHE20.CATAnalysis document presents the complete analysis of this case, computed with a mesh formed of parabolic hexahedron elements (HE20).
To compute the case with linear elements, proceed as follow:
-
Open one of the CATAnalysis documents.
-
Enter the Advanced Meshing Tools workbench.
-
In the specification tree, double-click the mesh:
-
Volume mesh for linear tetrahedron elements (TE4).
-
Surface mesh for linear hexahedron elements (HE8).
The Global Parameters dialog box appears.
-
-
Select the Linear element type.
-
Compute the case in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench.