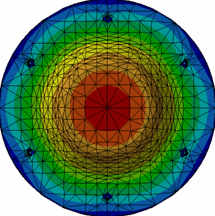
The purpose of this test is to compare a bolt tightening connection property and a virtual bolt tightening connection property. You will use 3D models.
Reference:
Comparison of the two models.
 Specifications
Specifications
Geometry Specifications
|
Bolt tightening connection property |
Virtual bolt tightening connection property |
|
|
|
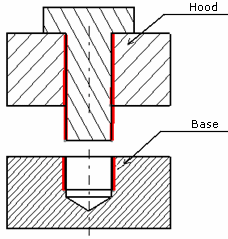
- Screw:
R1 = 35 mm
R2 = 20 mm
L1 = 15 mm
L2 = 120 mm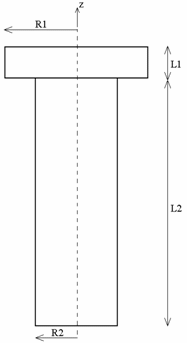
-
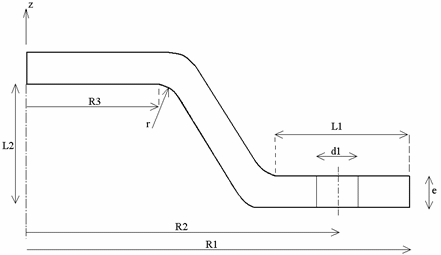
Hood:
R1 = 600 mm
R2 = 500 mm
R3 = 200 mm
L1 = 200 mm
L2 = 80 mm
r = 50 mm
d1 = 60 mm
e = 50 mm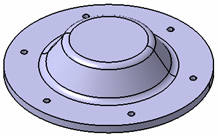
-
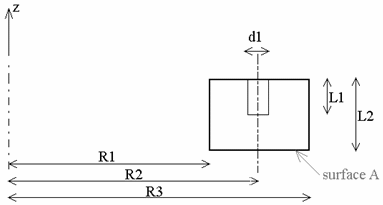
Base:
R1 = 400 mm
R2 = 500 mm
R3 = 600 mm
L1 = 70 mm
L2 = 140 mm
d1 = 40 mm
-
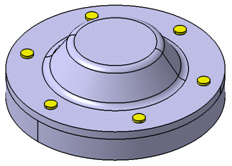
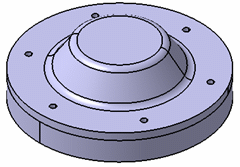
Assembly:
For the bolt connection property model, the hood, the base and six screws are assembled. For the virtual bolt connection property, only the hood and the base are assembled.
Bolt tightening connection property
Virtual bolt tightening connection property
Analysis Specifications
|
Young Modulus (material):
|
|
|
Poisson's Ratio (material):
|
|
|
Mesh Specifications:
|
|
|
Contact Connections:
|
|
|
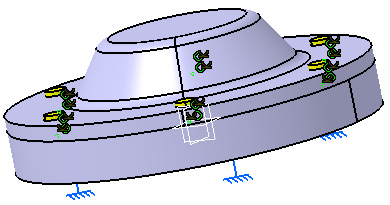
Restraints: The base is clamped on surface A |
|
|
Loads: |
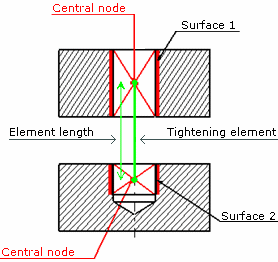
The stiffness of the virtual bolt's spring depends on the length of the spring element, not on the length of the bolt used in the bolt tightening connection property.
Stiffness is given by the formula:
![]()
So for each component:
- Translation stiffness 1: 9.91 x 107 N/m
- Translation stiffness 2: 9.91 x 107 N/m
- Translation stiffness 3: 1.3 x 109 N/m
- Rotation stiffness 1: 295566 N.m/rad
- Rotation stiffness 2: 295566 N.m/rad
- Rotation stiffness 3: 113636 N.m/rad
 Results
Results
The general shape is the same for the two models:
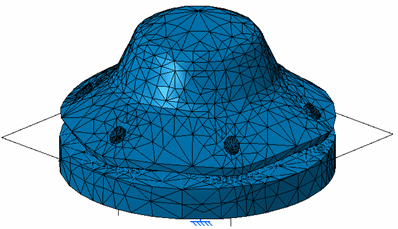
Values of maximum displacement are:
|
Bolt tightening connection |
Virtual bolt tightening connection |
Relative error |
|
|
|
-0.613 % |
|
Maximum displacement υ1 = 0.00816 mm |
Maximum displacement υ2 = 0.00811 mm |
You can also use parabolic tetrahedron elements (TE10). The difference is then -4.545 %
To Perform the Test:
The bolt_with_screw.CATAnalysis document presents a complete analysis of this case.
The bolt_without_screw.CATAnalysis document presents a complete analysis of this case.
To compute the case, proceed as follow:
-
Open the CATAnalysis document.
-
Compute the case in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench.