This test lets you validate the combined case. The aim is to compare a static case (where several forces are applied) and a combination of static cases (the set of forces of each static case is therefore equivalent to the one of the first configuration).
Reference:
-
AFNOR technique, SFM Paris, Guide de validation des progiciels de calcul de structures, SSLL 06/89, p30, 1990.
-
Results of the first configuration (all forces applied are located in one static case)
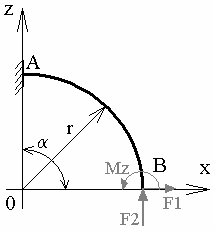
 Specifications
Specifications
Geometry Specifications
|
r = 3 m |
|
|
Hollow circular section: |
Analysis Specifications
| Young Modulus (material): E = 200 GPa |
 |
|
Mesh Specifications:
|
|
| Restraints: Clamp on A |
|
|
Loads:
|
 Results
Results
Analytical Solution
- At point B:
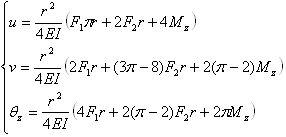
Sensors
Values
Translation displacements
uB (mm)379.1
Translation displacements
vB (mm)241.7
Rotation displacements
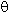 zB (rad)
zB (rad)0.1654
Computed Results
- Case computed with only one static case, gathering all applied forces:
Sensors
Values
uB (mm)
378.97885
vB (mm)
241.73313
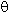 zB (rad)
zB (rad)0.165
-
Case computed with the combined case:
|
Sensors |
Analytic reference values |
One static case reference values |
Combined case values |
|
uB (mm) |
379.1 |
378.97885 |
378.97888 |
|
vB (mm) |
241.7 |
241.73313 |
241.73313 |
|
|
0.1654 |
0.165 |
0.165 |
To Perform the Test:
The thin_arc_combined.CATAnalysis document presents a complete analysis of this case.
The thin_arc_total.CATAnalysis document presents a complete analysis of this case.
To compute the case, proceed as follow:
-
Open one of the CATAnalysis document.
-
Compute the case in the Generative Structural Analysis workbench.
-
Create local sensors (Displacement vectors and Rotation vector).