 |
-
Select
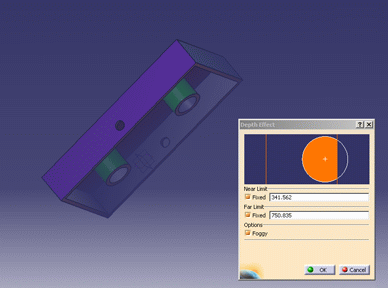
View > Depth Effect to display the Depth Effect
dialog box.
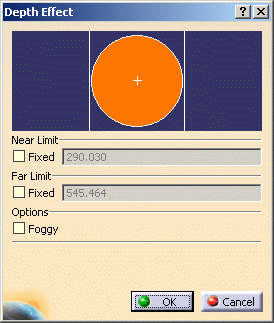 |
| The orange sphere
completely encompasses the objects in your document. The white
cross represents the center of the objects in the geometry area.
The color of the area behind the orange sphere is the background
color of your document.
The vertical lines represent the front (near) and back (far)
clipping planes. |
| By default, depth effects
are deactivated: if you zoom in and out, you will see that for the
moment the geometry is not clipped. |
 |
You can keep the Depth Effect
dialog box open and continue working with other commands. You will
be able to understand the results obtained by setting depth effects
by zooming in and out. |
-
Set the Near Limit and Far Limit by selecting the
Fixed check box for each option, entering values and pressing
Enter in each case.
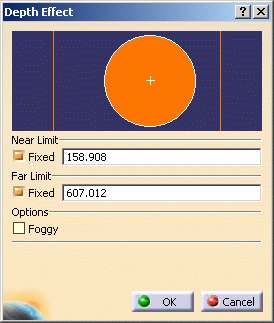 |
| Note that location of the vertical lines
representing the clipping planes has changed. |
| You can also drag
the vertical lines representing the near and far clipping planes to
produce the same effect. |
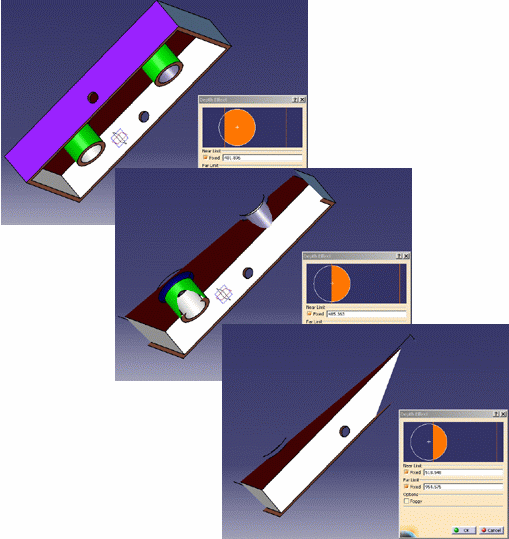 |
| The back (far) section of the geometry is clipped.
You now only see what is located between the near and far clipping
planes. |
 |
The Near Limit and Far Limit values can
change even when they are not activated because they are
dependent on the global bounding box of the 3D object. Whenever
the size of the bounding box exceeds the Near or Far Limit, the
values are adjusted accordingly. |
-
Zoom out to see all the geometry.
-
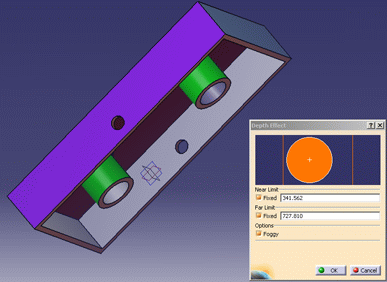
Select the Foggy check box.
| The foggy option introduces a foggy effect. |
 |
-
Zoom out again.
| As you zoom out, the fog effect is increased. The
fog gets thicker as you continue to zoom out beyond the back
clipping plane. |
 |
|