After restoration, the reporting tool, in a specific number of cases described below, will analyze the ENOVIA V5 VPM metadata, vault server metadata and vault server file systems in order to track broken links, and provides repair functions and correction proposals whenever possible.
Errors Tracked
The tool can track four types of errors broadly divided into two categories:
- dangling pointers
- unreferenced data.
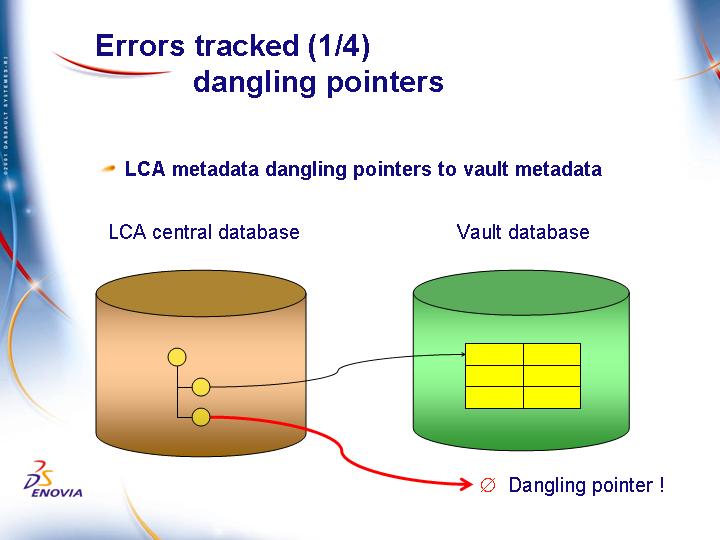
ENOVIA V5 VPM dangling pointers to vault metadata
This can occur after a vault database server crash. Any vault metadata created after the last backup will be missing in the restored vault database. But ENOVIA V5 VPM metadata still points to the data in the central ENOVIA V5 VPM database server.
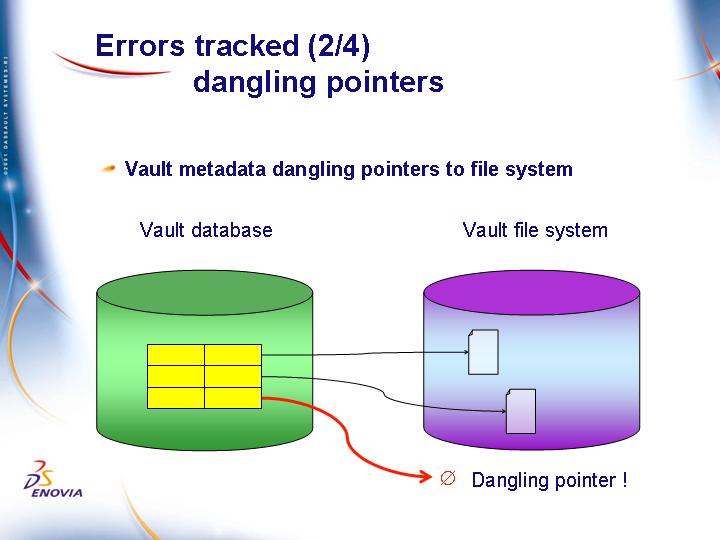
Vault metadata dangling pointers to file
This can occur:
- after a vault database server crash: any vault metadata deleted after the last backup will reappear after the restore of the crashed vault server but the pointed file has been deleted.
- after a vault file system crash: any vault file created after the last backup will be missing in the restored vault file system, but vault metadata still points to the data in the corresponding vault server database.
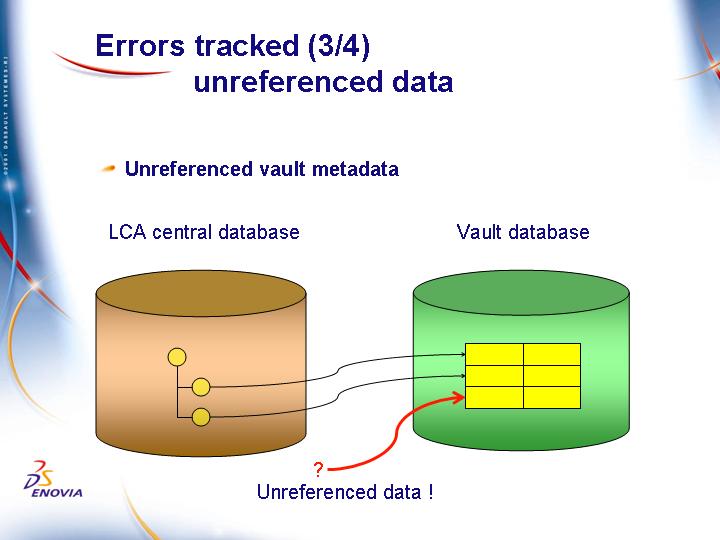
Unreferenced vault metadata
This can occur after a vault database server crash. Any vault metadata deleted after the last backup will reappear after the restore of the crashed vault server but the corresponding ENOVIA V5 VPM metadata is missing from the central ENOVIA V5 VPM database.
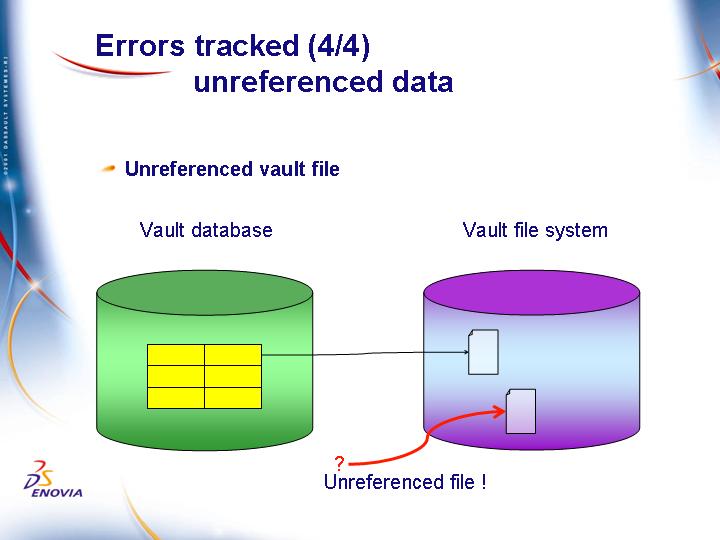
Unreferenced vault files
This can occur:
- after a vault database server crash: any vault metadata created after the last backup will be missing in the restored vault server but the corresponding vault file still exists in the vault file system.
- after a vault file system crash: any vault file deleted after the last backup will reappear after the restore of the crashed vault file system, but the corresponding vault metadata has been deleted from the vault database.
Running the Vault Link Checker
Run the vault link checker on the machine on which the vault server is installed (this is the vault server being checked) as follows:
./catstart -run "ENOCheckVaultLink.sh"
The arguments are:
ENOCheckVaultLink.sh [ -h | -TmpDir tmpdir -DatabaseVendor databaseVendor -DatabaseName databaseName -TableOwner tableOwner -ConnectUser connectUser -ConnectPasswd connectPasswd -FileOut fileOut[-ExceptVaultAlias exceptVaultAlias | -ListVaultAlias listVaultAlias ] [-ExceptDomain exceptDomain | -ListDomain listDomain] [-AfterTimeStamp afterTimeStamp] [-NOCorrection | -ONLYCorrection]
| Option | Optional/Mandatory | Description |
-TmpDir |
mandatory | A directory where the executables can read and write temporary data |
-DatabaseName |
mandatory | the connection string to the central database |
-DatabaseVendor |
mandatory | the database vendor [DB2 | ORACLE] |
-TableOwner |
mandatory | the database schema (on DB2) or the database structures owner (on ORACLE) |
-ConnectUser |
mandatory | the user to be used to connect on the central database, read/update data on the central database |
-ConnectPasswd |
mandatory | the password of the user used to connect to the central database |
-FileOut |
mandatory | The absolute name of the file that will be generated. The file has to be generated in a writable directory for the user that will launch the shell. |
-ExceptVaultAlias |
optional | Not yet supported. |
-ListVaultAlias |
mandatory | Enter the alias name of the restored
vault. This alias has to be found in the vault client properties. Only lists with one item are supported for the moment. This means one vault alias name, the alias name of the vault server which crashed. This alias is located in the VaultClient.properties file on the central ENOVIA V5 VPM server. |
-ExceptDomain |
optional | enter the name of data domains found in the admin data that are not to be checked |
-ListDomain |
optional | enter a list of the only data domains that are to be checked |
-AfterTimeStamp |
optional | enter a timestamp in the following format
(usual database time format):
this will check only the ENOVIA V5 VPM metadata modified after this timestamp. |
-NOCorrection |
optional | do not perform the correction step |
-ONLYCorrection |
optional | perform only the correction step (with the
info stored in the TmpDir from a previous Check run with the -NOCorrection
option). After the check, the tool only uses the information contained in the -TmpDir option but uses the file of the option -FileOut, obtained after first running the tool in -NOCorrection mode. |
|
|
optional |
displays help. |
Narrowing the Scope of Processing
You can narrow the scope of the processing performed by the tool as follows:
By a timeframe
The tool will use the LASTUPDATEDATE column to collect the vault links to check. Only dangling pointers to vault metadata or vault file systems will benefit from this option.
By a list of vault alias
Both LIST (…) and EXCEPT (…) options are available. The standard use is to narrow the process with the alias of the crashed vault.
By a list of domains
Both LIST (…) and EXCEPT (…) options are available. Only dangling pointers to vault metadata or vault file systems will benefit from this option.
Reporting tool steps
The tool performs the following steps:
- extracts all the vault links from the central ENOVIA V5 VPM database (optimized with narrowing capabilities)
- checks the consistency between the extracted links and the vault metadata and file system.
- tracks unreferenced vault metadata and files.
- outputs an XML format report containing the detected errors
- processes the correction proposals.
Understanding the Generated File
The output file generated contains XML tags describing the detected problems. There are 5 nodes that can appear in the XML file:
ROOTNODE
this tag aggregates all the other tags.
DANGLINGLCA (ENOVIA V5 VPM dangling pointers to vault metadata)
DANGLINGVAULT (Vault metadata dangling pointers to file)
UNREFVAULT (Unreferenced vault metadata)
UNREFFILE (Unreferenced vault files)
Correction Modes
The tool ENOCheckVaultLink command can be run in the following correction modes.
No automatic correction
No automatic correction of the detected problems. You must run the command using all the mandatory options (not just -NOCorrection). The XML output file will be generated in the -FileOut location. Along with the mandatory options, -NOCorrection must also be specified.
Automatic correction of the detected problems
To correct the detected problems automatically, you must run the command using all the mandatory options (but neither -ONLYCorrection nor -NOCorrection).
Note: automatic correction only corrects errors for unreferenced vault metadata and unreferenced vault files, as well as the correction that is applied.
Customize the desired corrections in the XML file
Run the tool in no automatic correction mode using all the mandatory options. Then, edit the XML file generated in the -FileOut location to specify the corrections you want to perform. Finally, rerun the command using the same options, except this time replace the -NOCorrection option by the -ONLYCorrection option.
Correction scope and Limitations
ENOVIA V5 VPM dangling pointers to vault metadata
The ENOVIA V5 VPM dangling pointers identified by the tool have to be manually repaired.
Vault metadata dangling pointers to file
The impacted vault metadata identified by the tool have to be manually repaired.
Unreferenced vault metadata
In this case, the tool will be able to automatically clean the vault database.
Unreferenced vault files
In this case, the tool will be able to automatically remove the files.
Return Codes for the Vault Link Checker
The return code is not meaningful to know if errors have been reported in the output file. It just indicates if all steps have been fully performed.
0 : all steps have been performed
1 : step 1 failed.
2 : step 2 failed
3 : step 3 failed.
100: bad arguments.
Repairing ENOVIA V5 VPM Dangling Pointers
There is a way to try to repair ENOVIA V5 VPM dangling pointers (which the Vault Link Checker cannot do).
Using a two-step process, the Vault Link Restore Utility makes propositions to repair the dangling pointers, and repairs the accepted ones.
During the first step, simulation, it uses the DANGLINGLCA tag in the Generated XML file, to access to the database and to generate an output XML file which proposes to:
- delete the Format
- delete the Iteration
- find a Preferred Iteration.
The command syntax of this simulation step is:
>CheckVaultLink_Restorator -user uuu -pwd ppp -role rrr -isimul
InSimul.xml -osimul OutSimul.xml
Here is an example of an OutSimul.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding='UTF-8' ?>
<!DOCTYPE docChange >
<DOCCHANGE>
<!--
**************************************************************************************
-->
<!-- * -->
<!-- * Warning :only authorized modifications are deletes of whole Document
Revision blocks -->
<!-- * -->
<!--
**************************************************************************************
-->
<!-- * -->
<!-- * Warning :if execution is succesfull ,this file will be renamed ,do
not re-use it -->
<!-- * ,restart a simulation -->
<!-- * -->
<!--
**************************************************************************************
-->
<DOCREV V_version="---" V_description="---" V_ID="PGR2" >
<ACTION Action="Delete" V_doc_iter_num="0" OID_MO="ACE4C6CE0014A0544048BF37000AF3E1"
TYPE_MO="80A2B3BD00000509384D10620005D1D1" DD_MO="454E4F44525F444F4344495220202020"
/>
</DOCREV>
</DOCCHANGE>
The Data Administrator chooses to accept some of the propositions by leaving them in the file and to refuse some others by deleting them from the file.
During the second step, execution, the Vault Link Restorator Utility reads the file reviewed by the Data Administrator, and applies the repair propositions.
The command syntax of this step is:
>CheckVaultLink_Restorator -user uuu -pwd ppp -role rrr -exec
InExec.xml
Note that the Generated file has evolved to a certain extent: for both DANGLINGLCA and DANGLINGVAULT, the tags are:
OID
TYPE
Attribute
TYPEOID new: hexadecimal value of the Type the pointing object
DATADOMAINOID new: hexadecimal value of the Data Domain the pointing
object
URL
VDOID
DOCLOCATION
DOCSIZE new: size (in bytes) of the pointed document
LASTUPDATEDATE new: last update date of the document
The shell arguments of ENOCheckVaultLink.sh have not changed.
![]()